We study evolutionary methods for the optimization of optical systems
The development of optical systems usually involves an optimization stage in which a set of parameters leading to maximum efficiency is sought. The complexity of these optimization problems increases exponentially with the number of parameters to be determined. We have developed evolutionary methods (genetic algorithms, PSO) to solve these optimization problems more efficiently.
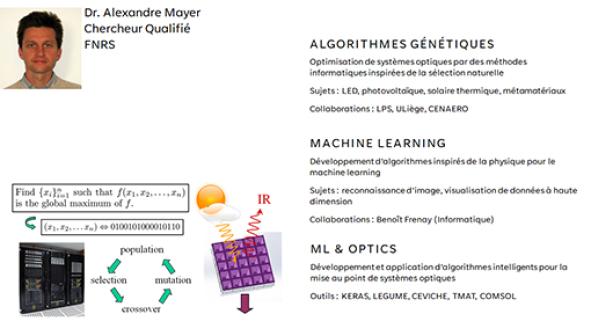
The general idea behind a genetic algorithm is to work with a population of individuals representing possible solutions to the problem under consideration. The best individuals are selected. Their parameters are subjected to crossover and mutation to determine new individuals for the next generation. This strategy is repeated from generation to generation until the population converges towards the global optimum of the problem.
A multi-objective genetic algorithm has been developed for the optimization of systems for which several objectives must be achieved. The genetic algorithm can be easily coupled with any external software used for modeling the system under consideration. It will run massively in parallel on CECI's supercomputers and on Tier-1, using the computing resources of the PTCI technology platform.
New algorithms are currently being developed. Among them, particle swarm optimization (PSO) is inspired by the dynamics of bird flocks. It is also used to determine the global optimum of problems.
Applications
Optimization of light-emitting diodes (LEDs), thermal solar panels, photovoltaic panels, metamaterial superabsorbers.
Representative publications
- A. Mayer, L. Gaouyat, D. Nicolay, T. Carletti and O. Deparis, Multi-objective genetic algorithm for the optimization of a flat-plate solar thermal collector, Optics Express 22, A1641 (2014)
- A. Mayer and A. Bay, Optimization by a genetic algorithm of the light-extraction efficiency of a GaN light-emitting diode, Journal of Optics 17, 025002 (2015)
- A. Mayer, J. Muller, A. Herman and O. Deparis, Optimized absorption of solar radiations in nano-structured thin films of crystalline silicon via a genetic algorithm, Proceedings of SPIE 9546, 95461N-01 (2015)
- A. Razzaq, A. Mayer, V. Depauw, I. Gordon, A.T. Hajjiah and J. Poortmans, Application of a genetic algorithm in four-terminal perovskite/crystalline-silicon tandem devices, IEEE Journal of Photovoltaics 10, 1689 (2020)
- A. Mayer, H. Bi, S. Griesse-Nascimento, B. Hackens, J. Loicq, E. Mazur, O. Deparis and M. Lobet, Genetic-algorithm-aided ultra-broadband perfect absorbers using plasmonic metamaterials, Optics Express 30, 1167 (2022)
- N. Roy, Ch. Beauthier and A. Mayer, Setup of a New Adaptive Fuzzy Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm, IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (2022)
Projects
- PhotoNVoltaics, Nanophotonics for ultra-thin crystalline silicon photovoltaics, EU Project H2020 FP7-Energy, 2012-2015
- Different collaborations on the optimization of optical systems are currently in progress.
Promoter(PI): Alexandre MAYER
Alexandre Mayer, a member of the LPS, is also affiliated with the NISM (Pôle de recherche HPC-MM).
Thesis topics (Pr. Alexandre Mayer)
- Evolving optimization methods for numerical physics problems
- Transposing techniques from physics to Machine Learning
- Applications of artificial intelligence techniques in physics


