Mathematics is an indispensable tool for understanding and solving many of the problems of everyday life, it forms the formal language for many disciplines and defines a science, with its methods and laws, to which genuine research is associated. The Mathematics Department has sought to reconcile these aspects by specializing in applied mathematics since its inception, in both teaching and research.
The Department of Mathematics is located in the Sciences-Arrupe building, occupying a wing on the third and fourth floors.
It is responsible for undergraduate, master's and doctoral courses in mathematics. It also teaches in other sections and faculties.
Find out more about the Mathematics Department
Spotlight
News

Alexandre Mauroy: "Mathematics are everywhere!
Alexandre Mauroy: "Mathematics are everywhere!
Alexandre Mauroy has been a professor and researcher in the Department of Mathematics for almost 10 years, working in the field of dynamical systems. He is also Director of the naXys Research Institute, which puts its expertise in complex systems at the service of UNamur researchers from all disciplines. Aware of the sometimes austere reputation of maths among the general public, Alexandre Mauroy works to demonstrate that this discipline is at the heart of today's technological and scientific challenges.
.

Alexandre Mauroy trained as a civil engineer. With a passion for mathematics, he embarked on an academic career that led him to specialize in the study of dynamic systems. A choice that reflects his taste for solving complex problems: "Dynamic systems are phenomena that evolve over time in a non-linear fashion, and do not obey the laws of proportionality. They therefore represent a real challenge for mathematicians, as their equations cannot be solved directly. And yet, non-linear systems are all around us, starting with the weather, our biological clock, road traffic or even the movement of a simple pendulum. So it's a very rich subject."
The Koopman operator or the mathematical magic wand
In his work, Alexandre Mauroy develops methods to better understand these dynamical systems. His stint at the University of Santa Barbara in California from 2011 to 2013 introduced him to operator theory, and in particular the Koopman operator, an original method for studying these unsolvable equations : "The idea may seem counter-intuitive, because we transform a finite-dimensional system into an infinite-dimensional one. It is then described by an infinite number of variables, but it becomes linear and can therefore be solved more easily. It's like using a kind of mathematical magic wand", he explains.
Koopman's operator is not new, however: it was first demonstrated in the 1930s before falling into oblivion. It was only revived in the 2000s. "It was the very beginning of the renaissance of this approach, we were pioneers", recalls Alexandre Mauroy. "Today, the Koopman operator has become very trendy in the scientific community."
And for good reason, many applications are possible thanks to this method. Among those studied by Alexandre Mauroy:
- The study of global stability of equilibria.
- The identification of network structure from observed data (e.g. connections between neurons in the brain or interactions between people).
- Control theory, halfway between mathematics and engineering sciences, which aims to impose the behavior of the dynamic system (e.g. car cruise control).
In this last field, Alexandre Mauroy is collaborating with Elio Tuci (Faculty of Computer Science) on the ARC "AUTOMATic" project, which aims to develop an intelligent urban traffic management system, thanks to data collected by drones. This project illustrates the interdisciplinary dimension of the naXys Institute's research and the "applied math" specificity of the teaching at UNamur's Mathematics Department, which is unique in the Wallonia-Brussels Federation.
.Dusting off the image of mathematics
In addition to his research activities, Alexandre Mauroy is involved in outreach work with secondary school students. The aim? To show that a world "without maths" would be very different from our own.

When we use Google, ChatGPT, or even when we watch Netflix, we use mathematical algorithms.
His message is clear: mathematics is everywhere, and mathematicians have a role to play alongside engineers and computer scientists, particularly in meeting the technological challenges of today and tomorrow.
.
From video games to artificial intelligence, a stopover in Japan
From video games to artificial intelligence, a stopover in Japan
Japan is almost 10,000 kilometers from Belgium, a country that fascinates, not least for its rich culture full of contrasts. Researchers at UNamur maintain close ties with several Japanese institutions, particularly in the fields of computer science, mathematics and video games. Let's take a look at some of these collaborations.
.
Japan is a world reference when it comes to video games. Nintendo, Sony, Sega... so many companies that have left their mark on contemporary popular culture. Fanny Barnabé knows this industry well. A lecturer at the Faculté Économie Management Communication sciencesPo (EMCP) and researcher at the CRIDS/NaDI research institute, she specializes in game studies, a field of research devoted to the study of games. After defending her doctoral thesis on videogame détournement in the fictional universe of Pokémon in 2017, she spent a year as a postdoctoral fellow at the Ritsumeikan Center For Game Studies (Ritsumeikan University, Kyoto), the archipelago's largest video game research center. Internationally recognized, the Center is fortunate to host an exceptional and unpublished archive, thanks to a donation from the giant Nintendo.
.Japan: fertile ground for game studies research
"This stay enabled me to make lasting contacts with the Center's researchers and to insert myself a little more into the somewhat niche field of Japanese video games", explains Fanny Barnabé. "Japan is home to top-flight, internationally recognized researchers, but also industry figures who are easily mobilized, thanks to the country's important position in terms of video game production."

Many years and research work later, Fanny Barnabé visited Japan once again at the end of May, on an academic mission. The aim: to present the latest work being carried out at UNamur, particularly in edutainment or "serious game"and, she hopes, lay the foundations for new partnerships and student exchanges.
Green AI in focus
The Faculty of Informatics has long-standing links with the National Institute of Informatics (NII), an internationally recognized research institute located in the heart of Tokyo. Each year, Master's and PhD students from the faculty are hosted there for a period of four to six months to carry out internships and research projects, via a specific collaboration agreement (Memorandum Of Understanding agreement, or MOU). It's an experience much appreciated by students and PhD students alike, on both scientific and human levels.
Gilles Perrouin, researcher and chairman of the Faculty of Computer Science's Research Commission, guides these students through the presentation of their research topic, often focused in the fields of software engineering, artificial intelligence (AI) or, more recently, green AI. "These are research fields that are evolving very quickly", Gilles Perrouin points out. "There's a lot of debate right now around AI's energy consumption. It's a bit of an oxymoron to say that we can do green AI.But we're working on it via the exploration of smarter techniques when looking for promising solutions to avoid resorting to systematic training of the neural network, which is very costly in terms of energy"explains the researcher. The collaboration has led to the exploration of other areas of AI, such as sign language recognition (Professor Benoît Frénay), in addition to topics in formal methods and software engineering (Professors Pierre-Yves Schobbens and Xavier Devroey).
The academic mission, which Gilles Perrouin also took part in May 2025, was aimed in particular at renewing the collaboration agreement with the NII, but also at sparking promising new partnerships in the fields of software engineering, AI, ethics or cybersecurity.

Dynamic systems under the microscope
At the heart of the Mathematics Department, Alexandre Mauroy, professor and researcher at the Namur Institute for Complex Systems (naXys), is working with his long-time collaborator and friend Yoshihiko Susuki from the prestigious University of Kyoto on a project co-funded by F.N.R.S and JSPS (Japan) to study dynamical systems. "These are so-called 'non-linear' phenomena that do not respect the rules of proportionality. The equations are therefore very difficult, if not impossible, to solve in practice, explains Alexandre Mauroy. "To get around this problem, we mobilize techniques like operator theory, which we're studying as part of this project." This has the advantage of combining theoretical aspects with practical applications, particularly in the field of electrical distribution networks. "These are complex systems, with slow and fast dynamics. An interesting case for which mathematical tools need to be adapted", continues Alexandre Mauroy. This first positive partnership has already led to research visits between the two countries, and promises new collaborations in the future.
In a related field, Riccardo Muolo has been a postdoctoral fellow at the Institute of Science Tokyo since 2023, after completing a PhD thesis at UNamur under the supervision of Professor Timoteo Carletti. Building on the knowledge acquired during his PhD on network dynamics, Riccardo Muolo is now interested in network synchronization theory, a mathematical model that enables us to understand a wide variety of systems: from fireflies to electrical networks to the functioning of the human brain: "For example, in the brain, abnormal synchronization of neuronal networks is associated with pathologies such as epilepsy or Parkinson's. The recent power grid failure in Spain can also be analyzed through this theory", details the researcher.
Student mobility
Students wishing to spend part of their degree course in Japan have the opportunity to do so, thanks to the various agreements UNamur has signed with Japanese institutions. This is the case with the National Institute of Informatics (NII), but also with Soka University and Sophia University (Chiyoda), with which UNamur has signed framework agreements.
This article is taken from the "Far away" section of Omalius magazine #35 (July 2025).


Two prestigious publications for our network dynamics researchers
Two prestigious publications for our network dynamics researchers
Maxime Lucas is an FNRS Research Fellow in the Department of Mathematics and a member of the naXys Institute. He works on complex systems within the "Network Dynamics" cluster headed by Professor Timoteo Carletti. He is co-author of two papers on complex systems, recently published in prestigious journals Nature Physics and Physical Reviews Letters.

Analysis of collective behavior in complex systems
The study of complex systems published in Physical Reviews Letters supports a growing trend that focuses more on analyzing the collective behavior of a system rather than discovering the underlying mechanisms of interaction.
When we observe a flock of starlings swirling through the sky in perfect coordination - a phenomenon known as murmuration - we witness the elegant interplay of individual actions creating collective behavior. In trying to understand these fascinating patterns, researchers can isolate simple rules based on an individual bird's field of view and the distance separating it from its neighbors, but there's always the question of whether the model actually captures the processes driving interactions between birds (Fig. 1).
This is a general problem in complex systems research, which comes down to distinguishing mechanisms (the rules governing interactions) from behaviors (the observable patterns that emerge).
Figure 1: In bird flocks, each bird chooses its movement according to the separation distance and flight orientation of its neighbors (left). These simple rules can produce complex patterns, such as starling "murmurations" (right). New research explores how mechanisms (individual rules) are linked to behaviors (collective patterns) in networks that represent complex systems.
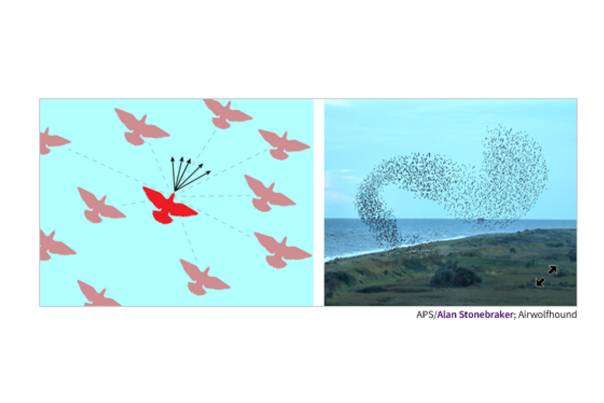
Representative networks of interacting individuals, or nodes, are a good way to study mechanisms versus behaviors. Until now, researchers have focused on pairwise interactions, but many systems also include higher-order interactions between several nodes. The impact of these higher-order mechanisms on behavior has not been clearly established. Thomas Robiglio, from the Central European University in Vienna, and his colleagues, including Maxime Lucas (CR FNRS - UNamur) addressed this question. They considered networks with higher-order interactions and evaluated the resulting behaviors in terms of statistical dependencies between node values.
The researchers identified higher-order behavioral signatures which, unlike their pairwise counterparts, reveal the presence of higher-order mechanisms. Their findings open up new avenues for distinguishing mechanisms and behaviors when studying complex systems - a distinction that is crucial for the study of inference in network science, neuroscience, the social sciences and beyond.
This study is also the subject of a "Featured in Physics" and "Editor's suggestion" article, and a "commentary" article at the journal's request, available on their website in English in full.
Namur Institute for Complex Systems (naXys)
The naXys institute specializes in the analysis of complex systems, whether in astronomy and dynamic cosmology, mathematical biology, optimization in optics, economic complexity or the study of the stability and robustness of these systems.


UNamur researchers published in Nature Physics
UNamur researchers published in Nature Physics
Professor Timoteo Carletti of the University of Namur has just published in the prestigious journal Nature Physics in collaboration with Professor Ginestra Bianconi of Queen Mary University of London and eight other international researchers. This groundbreaking study could lead to the development of new AI algorithms, new ways of studying brain function, or breakthroughs in disciplines such as physics, climate science, finance and many others.

The study, entitled "Topology shapes dynamics of higher-order networks" proposes a theoretical framework specifically designed to understand complex higher-order networks where several agents interact at the same time and thus generalize networks with their interactions in pairs. More precisely, the study shows how topology shapes dynamics, how dynamics learns topology and how topology evolves dynamically.
The aim of this work is to introduce physicists, mathematicians, computer scientists and network scientists to this emerging research field, as well as to define future research challenges where discrete topology and nonlinear dynamics mix.
With the data in their possession, the researchers show that real-life complex systems such as the brain, chemical reactions and neural networks can be easily modeled as higher-order networks, characterized by multi-body connections indicating the fact that several elements of the system interact simultaneously.
This international team is convinced that the visibility of their work through this publication in Nature Physics will open the door to new collaborations with other disciplines that rely on network analysis to study real complex systems.
Kudos to the team for this publication!
Timoteo Carletti - Mini CV
After a Master's degree in physics (University of Florence, June 1995), Timoteo Carletti pursued his doctoral studies in Florence (Italy) and Paris (France) at IMCCE, finally defending his doctoral thesis in mathematics in February 2000.
He moved to Belgium in 2005, and was hired at the University of Namur as a lecturer, then as a professor (2008), and finally as a full professor (2011) in the Mathematics Department of the Faculty of Science. In 2010, he was one of the founders of the Namur Center for Complex Systems (now the Namur Institute for Complex Systems - naXys), which he headed until December 2014.
.
Alexandre Mauroy: "Mathematics are everywhere!
Alexandre Mauroy: "Mathematics are everywhere!
Alexandre Mauroy has been a professor and researcher in the Department of Mathematics for almost 10 years, working in the field of dynamical systems. He is also Director of the naXys Research Institute, which puts its expertise in complex systems at the service of UNamur researchers from all disciplines. Aware of the sometimes austere reputation of maths among the general public, Alexandre Mauroy works to demonstrate that this discipline is at the heart of today's technological and scientific challenges.
.

Alexandre Mauroy trained as a civil engineer. With a passion for mathematics, he embarked on an academic career that led him to specialize in the study of dynamic systems. A choice that reflects his taste for solving complex problems: "Dynamic systems are phenomena that evolve over time in a non-linear fashion, and do not obey the laws of proportionality. They therefore represent a real challenge for mathematicians, as their equations cannot be solved directly. And yet, non-linear systems are all around us, starting with the weather, our biological clock, road traffic or even the movement of a simple pendulum. So it's a very rich subject."
The Koopman operator or the mathematical magic wand
In his work, Alexandre Mauroy develops methods to better understand these dynamical systems. His stint at the University of Santa Barbara in California from 2011 to 2013 introduced him to operator theory, and in particular the Koopman operator, an original method for studying these unsolvable equations : "The idea may seem counter-intuitive, because we transform a finite-dimensional system into an infinite-dimensional one. It is then described by an infinite number of variables, but it becomes linear and can therefore be solved more easily. It's like using a kind of mathematical magic wand", he explains.
Koopman's operator is not new, however: it was first demonstrated in the 1930s before falling into oblivion. It was only revived in the 2000s. "It was the very beginning of the renaissance of this approach, we were pioneers", recalls Alexandre Mauroy. "Today, the Koopman operator has become very trendy in the scientific community."
And for good reason, many applications are possible thanks to this method. Among those studied by Alexandre Mauroy:
- The study of global stability of equilibria.
- The identification of network structure from observed data (e.g. connections between neurons in the brain or interactions between people).
- Control theory, halfway between mathematics and engineering sciences, which aims to impose the behavior of the dynamic system (e.g. car cruise control).
In this last field, Alexandre Mauroy is collaborating with Elio Tuci (Faculty of Computer Science) on the ARC "AUTOMATic" project, which aims to develop an intelligent urban traffic management system, thanks to data collected by drones. This project illustrates the interdisciplinary dimension of the naXys Institute's research and the "applied math" specificity of the teaching at UNamur's Mathematics Department, which is unique in the Wallonia-Brussels Federation.
.Dusting off the image of mathematics
In addition to his research activities, Alexandre Mauroy is involved in outreach work with secondary school students. The aim? To show that a world "without maths" would be very different from our own.

When we use Google, ChatGPT, or even when we watch Netflix, we use mathematical algorithms.
His message is clear: mathematics is everywhere, and mathematicians have a role to play alongside engineers and computer scientists, particularly in meeting the technological challenges of today and tomorrow.
.
From video games to artificial intelligence, a stopover in Japan
From video games to artificial intelligence, a stopover in Japan
Japan is almost 10,000 kilometers from Belgium, a country that fascinates, not least for its rich culture full of contrasts. Researchers at UNamur maintain close ties with several Japanese institutions, particularly in the fields of computer science, mathematics and video games. Let's take a look at some of these collaborations.
.
Japan is a world reference when it comes to video games. Nintendo, Sony, Sega... so many companies that have left their mark on contemporary popular culture. Fanny Barnabé knows this industry well. A lecturer at the Faculté Économie Management Communication sciencesPo (EMCP) and researcher at the CRIDS/NaDI research institute, she specializes in game studies, a field of research devoted to the study of games. After defending her doctoral thesis on videogame détournement in the fictional universe of Pokémon in 2017, she spent a year as a postdoctoral fellow at the Ritsumeikan Center For Game Studies (Ritsumeikan University, Kyoto), the archipelago's largest video game research center. Internationally recognized, the Center is fortunate to host an exceptional and unpublished archive, thanks to a donation from the giant Nintendo.
.Japan: fertile ground for game studies research
"This stay enabled me to make lasting contacts with the Center's researchers and to insert myself a little more into the somewhat niche field of Japanese video games", explains Fanny Barnabé. "Japan is home to top-flight, internationally recognized researchers, but also industry figures who are easily mobilized, thanks to the country's important position in terms of video game production."

Many years and research work later, Fanny Barnabé visited Japan once again at the end of May, on an academic mission. The aim: to present the latest work being carried out at UNamur, particularly in edutainment or "serious game"and, she hopes, lay the foundations for new partnerships and student exchanges.
Green AI in focus
The Faculty of Informatics has long-standing links with the National Institute of Informatics (NII), an internationally recognized research institute located in the heart of Tokyo. Each year, Master's and PhD students from the faculty are hosted there for a period of four to six months to carry out internships and research projects, via a specific collaboration agreement (Memorandum Of Understanding agreement, or MOU). It's an experience much appreciated by students and PhD students alike, on both scientific and human levels.
Gilles Perrouin, researcher and chairman of the Faculty of Computer Science's Research Commission, guides these students through the presentation of their research topic, often focused in the fields of software engineering, artificial intelligence (AI) or, more recently, green AI. "These are research fields that are evolving very quickly", Gilles Perrouin points out. "There's a lot of debate right now around AI's energy consumption. It's a bit of an oxymoron to say that we can do green AI.But we're working on it via the exploration of smarter techniques when looking for promising solutions to avoid resorting to systematic training of the neural network, which is very costly in terms of energy"explains the researcher. The collaboration has led to the exploration of other areas of AI, such as sign language recognition (Professor Benoît Frénay), in addition to topics in formal methods and software engineering (Professors Pierre-Yves Schobbens and Xavier Devroey).
The academic mission, which Gilles Perrouin also took part in May 2025, was aimed in particular at renewing the collaboration agreement with the NII, but also at sparking promising new partnerships in the fields of software engineering, AI, ethics or cybersecurity.

Dynamic systems under the microscope
At the heart of the Mathematics Department, Alexandre Mauroy, professor and researcher at the Namur Institute for Complex Systems (naXys), is working with his long-time collaborator and friend Yoshihiko Susuki from the prestigious University of Kyoto on a project co-funded by F.N.R.S and JSPS (Japan) to study dynamical systems. "These are so-called 'non-linear' phenomena that do not respect the rules of proportionality. The equations are therefore very difficult, if not impossible, to solve in practice, explains Alexandre Mauroy. "To get around this problem, we mobilize techniques like operator theory, which we're studying as part of this project." This has the advantage of combining theoretical aspects with practical applications, particularly in the field of electrical distribution networks. "These are complex systems, with slow and fast dynamics. An interesting case for which mathematical tools need to be adapted", continues Alexandre Mauroy. This first positive partnership has already led to research visits between the two countries, and promises new collaborations in the future.
In a related field, Riccardo Muolo has been a postdoctoral fellow at the Institute of Science Tokyo since 2023, after completing a PhD thesis at UNamur under the supervision of Professor Timoteo Carletti. Building on the knowledge acquired during his PhD on network dynamics, Riccardo Muolo is now interested in network synchronization theory, a mathematical model that enables us to understand a wide variety of systems: from fireflies to electrical networks to the functioning of the human brain: "For example, in the brain, abnormal synchronization of neuronal networks is associated with pathologies such as epilepsy or Parkinson's. The recent power grid failure in Spain can also be analyzed through this theory", details the researcher.
Student mobility
Students wishing to spend part of their degree course in Japan have the opportunity to do so, thanks to the various agreements UNamur has signed with Japanese institutions. This is the case with the National Institute of Informatics (NII), but also with Soka University and Sophia University (Chiyoda), with which UNamur has signed framework agreements.
This article is taken from the "Far away" section of Omalius magazine #35 (July 2025).


Two prestigious publications for our network dynamics researchers
Two prestigious publications for our network dynamics researchers
Maxime Lucas is an FNRS Research Fellow in the Department of Mathematics and a member of the naXys Institute. He works on complex systems within the "Network Dynamics" cluster headed by Professor Timoteo Carletti. He is co-author of two papers on complex systems, recently published in prestigious journals Nature Physics and Physical Reviews Letters.

Analysis of collective behavior in complex systems
The study of complex systems published in Physical Reviews Letters supports a growing trend that focuses more on analyzing the collective behavior of a system rather than discovering the underlying mechanisms of interaction.
When we observe a flock of starlings swirling through the sky in perfect coordination - a phenomenon known as murmuration - we witness the elegant interplay of individual actions creating collective behavior. In trying to understand these fascinating patterns, researchers can isolate simple rules based on an individual bird's field of view and the distance separating it from its neighbors, but there's always the question of whether the model actually captures the processes driving interactions between birds (Fig. 1).
This is a general problem in complex systems research, which comes down to distinguishing mechanisms (the rules governing interactions) from behaviors (the observable patterns that emerge).
Figure 1: In bird flocks, each bird chooses its movement according to the separation distance and flight orientation of its neighbors (left). These simple rules can produce complex patterns, such as starling "murmurations" (right). New research explores how mechanisms (individual rules) are linked to behaviors (collective patterns) in networks that represent complex systems.

Representative networks of interacting individuals, or nodes, are a good way to study mechanisms versus behaviors. Until now, researchers have focused on pairwise interactions, but many systems also include higher-order interactions between several nodes. The impact of these higher-order mechanisms on behavior has not been clearly established. Thomas Robiglio, from the Central European University in Vienna, and his colleagues, including Maxime Lucas (CR FNRS - UNamur) addressed this question. They considered networks with higher-order interactions and evaluated the resulting behaviors in terms of statistical dependencies between node values.
The researchers identified higher-order behavioral signatures which, unlike their pairwise counterparts, reveal the presence of higher-order mechanisms. Their findings open up new avenues for distinguishing mechanisms and behaviors when studying complex systems - a distinction that is crucial for the study of inference in network science, neuroscience, the social sciences and beyond.
This study is also the subject of a "Featured in Physics" and "Editor's suggestion" article, and a "commentary" article at the journal's request, available on their website in English in full.
Namur Institute for Complex Systems (naXys)
The naXys institute specializes in the analysis of complex systems, whether in astronomy and dynamic cosmology, mathematical biology, optimization in optics, economic complexity or the study of the stability and robustness of these systems.


UNamur researchers published in Nature Physics
UNamur researchers published in Nature Physics
Professor Timoteo Carletti of the University of Namur has just published in the prestigious journal Nature Physics in collaboration with Professor Ginestra Bianconi of Queen Mary University of London and eight other international researchers. This groundbreaking study could lead to the development of new AI algorithms, new ways of studying brain function, or breakthroughs in disciplines such as physics, climate science, finance and many others.

The study, entitled "Topology shapes dynamics of higher-order networks" proposes a theoretical framework specifically designed to understand complex higher-order networks where several agents interact at the same time and thus generalize networks with their interactions in pairs. More precisely, the study shows how topology shapes dynamics, how dynamics learns topology and how topology evolves dynamically.
The aim of this work is to introduce physicists, mathematicians, computer scientists and network scientists to this emerging research field, as well as to define future research challenges where discrete topology and nonlinear dynamics mix.
With the data in their possession, the researchers show that real-life complex systems such as the brain, chemical reactions and neural networks can be easily modeled as higher-order networks, characterized by multi-body connections indicating the fact that several elements of the system interact simultaneously.
This international team is convinced that the visibility of their work through this publication in Nature Physics will open the door to new collaborations with other disciplines that rely on network analysis to study real complex systems.
Kudos to the team for this publication!
Timoteo Carletti - Mini CV
After a Master's degree in physics (University of Florence, June 1995), Timoteo Carletti pursued his doctoral studies in Florence (Italy) and Paris (France) at IMCCE, finally defending his doctoral thesis in mathematics in February 2000.
He moved to Belgium in 2005, and was hired at the University of Namur as a lecturer, then as a professor (2008), and finally as a full professor (2011) in the Mathematics Department of the Faculty of Science. In 2010, he was one of the founders of the Namur Center for Complex Systems (now the Namur Institute for Complex Systems - naXys), which he headed until December 2014.
.







