Bachelor in Mathematics
-
Schedule
regular course
- ECTS Credits 180

Your bachelor's degree starts with a solid grounding in general mathematics (logic, analysis, algebra, geometry and probability).
Rapidly, you are confronted with current issues in applied mathematics through specialization courses in optimization, control, statistics, networks and dynamic systems.
Your training is open to other disciplines such as economics, management, computer science and the sciences. In fact, once you've completed your bachelor's degree in mathematical sciences, you'll have easy access to master's degrees in other disciplines (master's degrees in computer science and economics).
Throughout the bachelor's degree, you receive advanced training in scientific programming and develop your understanding of English to read and write scientific articles.
A human dimension completes your bachelor's degree with a reflective approach to the role and impact of science in society.

You're off to a good start
- you enjoy manipulating formulas;
- you feel at ease with mathematics;
- you demonstrate rigor and abstraction in your reasoning;
- you enjoy solving concrete problems.
Teaching methods
Courses, exercise sessions, practical work, computer programming workshops... everything is done to ensure your mastery of concepts and develop your skills in communication, autonomy, organization, teamwork, inventiveness, critical thinking and scientific research.
Organized in small teams (3 to 5 students) and supervised by an assistant, group work allows you to delve deeper into some of the material on your own.
Thanks to the "student-researcher" project, you can learn about research under the supervision of a departmental researcher. This experience also enables you to develop your autonomy, creativity and critical thinking skills.

As part of our innovative educational projects, as part of the Astronomy course, you will carry out observation evenings from the dome of the Antoine Thomas Astronomical Observatory located in the center of the campus. You build an observation project that you present as if it were an animation for the general public.
You complete your training by carrying out an interdisciplinary project. This project linked to applied mathematics includes a personal research and writing part followed by a collective part. Exhibitions, lectures, interactive games, journal writing - this project takes many forms and aims to develop your initiative, organizational skills and oral and written communication abilities. The work produced is presented as part of Printemps des Sciences.
Success aids
Succeeding in a year of study at university involves many challenges.
To help you meet them, UNamur supports you in developing your disciplinary, methodological and human skills... with the support of numerous professionals.
Preparatory courses, individualized help... Discover the schemes set up for your training.
After the baccalauréat: the master's degree
The University of Namur is organizing:
- the master 120 in mathematical sciences
- the master 60 in mathematical sciences
- the master in mathematics education
- 120 credits - section 4 (from 2025)
- 60 credits - section 5 (from 2025)
directly accessible after obtaining your bachelor's degree in mathematical sciences.
If you acquired the credits for the "economics and management" option during your bachelor's degree in mathematics, you can access the masters in economics at the University of Namur.
If you acquired the credits for the "scientific programming" option during your bachelor's degree in mathematics, you can access the masters in computer science at the University of Namur.
-
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Th.+Ex. Credits/Block 1 2 3 SMATB102 Real analysis II Winkin Joseph 30h th. + 32.5h ex. 7 SMATB107 Linear Algebra and Analytic Geometry Fuzfa André 30h th. + 32h ex. 5 SMATB202 Advanced algebra Mauroy Alexandre 15h th. + 19h ex. 3 SMATB240 Linear algebra II Daquin Jérôme 22h th. + 26h ex. 3 SMATB203_P34626 Complex analysis Carletti Timoteo 22.5h th. + 26.5h ex. 5 SMATB307 Symplectic geometry Libert Anne-Sophie 22.5h th. + 15h ex. 5 SMATB301_P36525 Analyse fonctionnelle - Partim Winkin Joseph 30h th. + 22.5h ex. 5 SMATB302_P36415 <unknown> Winkin Joseph 30h th. + 30h ex. 5 SMATB112 Introduction to mathematical thinking Libert Anne-Sophie 30h th. + 30h ex. 5 SMATB214 Differential Geometry Fuzfa André 30h th. + 22.5h ex. 4 SMATB101 Linear algebra Mauroy Alexandre 30h th. + 32h ex. 5 SMATB216 General Topology Winkin Joseph 15h th. + 19h ex. 3 SMATB103 Real analysis Winkin Joseph 30h th. + 32.5h ex. 7 SMATB222 Ordinary Differential Equations Carletti Timoteo 30h th. + 22.5h ex. 5 SECOB201 Economy De Crombrugghe De Picquendaele Alain 30h th. + 7.5h ex. 3 SMATB254 Graph Theory Franco Nicolas 30h th. + 22.5h ex. 5 -
<unknown>
-
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Th.+Ex. Credits/Block 1 2 3 SPHYB124_P35420 General physics: Mechanics HEUSKIN Anne-Catherine 55h th. + 24h ex. 8 Soft skillsSMATB213 Astronomie Fuzfa André DUBOIS Eve-Aline 15h th. 2 -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Th.+Ex. Credits/Block 1 2 3 SSPSB101 Philosophical questions Sartenaer Olivier Modera Astrid 22.5h th. + 7.5h ex. 2 Translated with DeepL.com (free version)SSPSB102 Religious Studies: Anthropology, Metaphysics and Science Leyens Stéphane Cazalis Roland 30h th. 2 -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Th.+Ex. Credits/Block 1 2 3 SSPSB204 Logic and argumentation Sartenaer Olivier Sartenaer Olivier 22.5h th. 2 SSPSB202 History of science Sartenaer Olivier 22.5h th. 2 SSPSB203 Psychology Ravez Laurent 22.5h th. 2 SSPSB307 Formal logic Sartenaer Olivier 15h th. 2 SSPSB308 Philosophy of science Sartenaer Olivier 15h th. 2 SSPSB309 Ethical Leyens Stéphane LAURENT Nathanaël 15h th. 2
-
-
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Th.+Ex. Credits/Block 1 2 3 Soft skillsSELVB304 English, maths and communication (level B2 and above) Zimmer Carole 30h th. 3 SELVB104 Introduction to Scientific English (level B1 and above) Zimmer Carole 30h th. 3 SELVB204 English and maths (level B1 and above) Zimmer Carole 30h th. 3 -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Th.+Ex. Credits/Block 1 2 3 SMATB243 Introduction to Space Sciences Dupal Jérémie Zimmer Carole Fuzfa André 3
-
-
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Th.+Ex. Credits/Block 1 2 3 INFOB126 Computer Architecture Schumacher Laurent 30h th. + 15h ex. 6 6 SPHYB126_P35423 General physics: Electricity Sporken Robert 50h th. + 21h ex. 6 -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Th.+Ex. Credits/Block 1 2 3 FINT0050 Space for Society Fuzfa André 24h th. 3 3 FINT0048 Artificial intelligence: challenges and opportunities Frenay Benoît 24h th. 3 3 Soft skillsFINT0049 Science for all : Effective science communication in English Hansel Aude Schutz Natassia 24h th. 3 3 -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Th.+Ex. Credits/Block 1 2 3 SMATB318 Introduction to the didactics of mathematics Dubussy Christophe 30h th. + 30h ex. 5 -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Th.+Ex. Credits/Block 1 2 3 SMATB210 Mathematical tools for modeling Mauroy Alexandre 30h th. + 22.5h ex. 5 SMATB334 Problem solving and mathematical modelling Mauroy Alexandre 30h th. + 22.5h ex. 5 SMATB325 Regression models Kiriliouk Anna 30h th. + 22.5h ex. 5 -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Th.+Ex. Credits/Block 1 2 3 INFOB234 Object-oriented design and programming Heymans Patrick 30h th. + 30h ex. 5 INFOB126 Computer Architecture Schumacher Laurent 30h th. + 15h ex. 6 6 Soft skillsINFOB212 Database Engineering Cleve Anthony 45h th. + 15h ex. 5 INFOB313 Analysis and Modelling of Information Systems Heymans Patrick Amrani Moussa 30h th. + 30h ex. 5 -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Th.+Ex. Credits/Block 1 2 3 SBIOB219 Biology Messiaen Johan 30h th. 5 SBIOB003 Pluridisciplinary scientific field trip Yans Johan Silvestre Frédéric Yans Johan Silvestre Frédéric 48h th. + 48h ex. 3 3 SPHYB209 Electrodynamics I Deparis Olivier Deparis Olivier 30h th. + 15h ex. 5 SGOLB313_P33839 Geophysics Louette Pierre Collinet Max 15h th. + 15h ex. 3 SCHIB309 Mathematical chemistry Champagne Benoît 30h th. + 22.5h ex. 5 SGOGB314 Climatology Houssiau Laurent 30h th. + 40h ex. 5 -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Th.+Ex. Credits/Block 1 2 3 EFASB357 Macroeconomics Kiedaisch Christian 45h th. 5 EFASB354 Financial and cost accounting Cerrada Cristia Karine Giot Pierre Cerrada Cristia Karine Danaux Géraldine 45h th. 5 ECGEB375 International economic relations De Crombrugghe De Picquendaele Alain 30h th. + 15h ex. 5 ECGEB383 Finance Giot Pierre SOUDANT Joey 45h th. + 15h ex. 5 -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Th.+Ex. Credits/Block 1 2 3 SMATB292 Student researcher project Q1-Q2 Henry Valérie 10 SMATB290 Student-researcher" project Q2 Henry Valérie 5 SMATB291 Student-researcher" project Q1 Henry Valérie 5 SMATB392 Student researcher project Q1-Q2 Henry Valérie 10 SMATB390 Student-researcher" project Q2 Henry Valérie 5 SMATB391 Student-researcher" project Q1 Henry Valérie 5
-
-
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 SMATB102 Real analysis II Winkin Joseph 7 30h th. + 32.5h ex. SMATB107 Linear Algebra and Analytic Geometry Fuzfa André 5 30h th. + 32h ex. SMATB112 Introduction to mathematical thinking Libert Anne-Sophie 5 30h th. + 30h ex. SMATB101 Linear algebra Mauroy Alexandre 5 30h th. + 32h ex. SMATB103 Real analysis Winkin Joseph 7 30h th. + 32.5h ex. -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 SMATB109 Discrete Probability Theory Franco Nicolas 4 22.5h th. + 22.5h ex. SINFB103 Programming I Tuci Elio 3 30h th. + 16h ex. SINFB104 Programming II Tuci Elio 3 19h ex. -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 SPHYB124_P35420 General physics: Mechanics HEUSKIN Anne-Catherine 8 55h th. + 24h ex. -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 SSPSB101 Philosophical questions Sartenaer Olivier Modera Astrid 2 22.5h th. + 7.5h ex. Translated with DeepL.com (free version)SSPSB102 Religious Studies: Anthropology, Metaphysics and Science Leyens Stéphane Cazalis Roland 2 30h th. -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 SELVB104 Introduction to Scientific English (level B1 and above) Zimmer Carole 3 15h th. 15h th. -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 INFOB126 Computer Architecture Schumacher Laurent 6 30h th. + 15h ex. SPHYB126_P35423 General physics: Electricity Sporken Robert 6 50h th. + 21h ex.
-
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 SMATB202 Advanced algebra Mauroy Alexandre 3 15h th. + 19h ex. SMATB240 Linear algebra II Daquin Jérôme 3 22h th. + 26h ex. SMATB203_P34626 Complex analysis Carletti Timoteo 5 22.5h th. + 26.5h ex. SMATB214 Differential Geometry Fuzfa André 4 30h th. + 22.5h ex. SMATB216 General Topology Winkin Joseph 3 15h th. + 19h ex. SMATB222 Ordinary Differential Equations Carletti Timoteo 5 30h th. + 22.5h ex. SECOB201 Economy De Crombrugghe De Picquendaele Alain 3 30h th. + 7.5h ex. SMATB254 Graph Theory Franco Nicolas 5 30h th. + 22.5h ex. -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 SMATB211 Statistics Van Bever Germain 5 30h th. + 22.5h ex. SMATB208 Point and solid mechanics Libert Anne-Sophie Coyette Alexis 3 22.5h th. + 22.5h ex. SINFB206 Programming project Tuci Elio 2 7h th. + 15h ex. SINFB207 Advanced programming Tuci Elio HUBERMONT Antoine 2 22h th. + 15h ex. -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 Soft skillsSMATB213 Astronomie Fuzfa André DUBOIS Eve-Aline 2 7.5h th. 7.5h th. -
<unknown>
-
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 SSPSB204 Logic and argumentation Sartenaer Olivier Sartenaer Olivier 2 22.5h th. SSPSB202 History of science Sartenaer Olivier 2 22.5h th. SSPSB203 Psychology Ravez Laurent 2 22.5h th.
-
-
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 SELVB204 English and maths (level B1 and above) Zimmer Carole 3 15h th. 15h th. -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 SMATB243 Introduction to Space Sciences Dupal Jérémie Zimmer Carole Fuzfa André 3
-
-
<unknown>
-
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 FINT0050 Space for Society Fuzfa André 3 24h th. FINT0048 Artificial intelligence: challenges and opportunities Frenay Benoît 3 24h th. Soft skillsFINT0049 Science for all : Effective science communication in English Hansel Aude Schutz Natassia 3 12h th. 12h th. -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 SMATB210 Mathematical tools for modeling Mauroy Alexandre 5 30h th. + 22.5h ex. -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 INFOB234 Object-oriented design and programming Heymans Patrick 5 30h th. + 30h ex. INFOB126 Computer Architecture Schumacher Laurent 6 30h th. + 15h ex. -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 SBIOB219 Biology Messiaen Johan 5 30h th. SBIOB003 Pluridisciplinary scientific field trip Yans Johan Silvestre Frédéric Yans Johan Silvestre Frédéric 3 48h th. + 48h ex. SPHYB209 Electrodynamics I Deparis Olivier Deparis Olivier 5 30h th. + 15h ex. -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 EFASB357 Macroeconomics Kiedaisch Christian 5 45h th. EFASB354 Financial and cost accounting Cerrada Cristia Karine Giot Pierre Cerrada Cristia Karine Danaux Géraldine 5 45h th. -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 SMATB292 Student researcher project Q1-Q2 Henry Valérie 10 SMATB290 Student-researcher" project Q2 Henry Valérie 5 SMATB291 Student-researcher" project Q1 Henry Valérie 5
-
-
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 SMATB307 Symplectic geometry Libert Anne-Sophie 5 22.5h th. + 15h ex. SMATB301_P36525 Analyse fonctionnelle - Partim Winkin Joseph 5 30h th. + 22.5h ex. SMATB302_P36415 <unknown> Winkin Joseph 5 30h th. + 30h ex. -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 SMATB315 Mathematical algorithms for scientific computing Franco Nicolas 5 30h th. + 45h ex. SMATB317 Partial differential equations and numerical methods Dubussy Christophe Fuzfa André 5 30h th. + 22.5h ex. SMATB304 Optimization Sartenaer Annick 5 30h th. + 22.5h ex. SMATB305 Probability II Swan Yves-Caoimhin Van Bever Germain 5 30h th. + 22.5h ex. SMATB303 Numerical analysis Sartenaer Annick Berger Guillaume 5 30h th. + 22.5h ex. SMATB310 Interdisciplinary work Daquin Jérôme 5 15h th. + 15h ex. -
<unknown>
-
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 SSPSB307 Formal logic Sartenaer Olivier 2 15h th. SSPSB308 Philosophy of science Sartenaer Olivier 2 15h th. SSPSB309 Ethical Leyens Stéphane LAURENT Nathanaël 2 15h th.
-
-
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 Soft skillsSELVB304 English, maths and communication (level B2 and above) Zimmer Carole 3 15h th. 15h th. -
<unknown>
-
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 FINT0050 Space for Society Fuzfa André 3 24h th. Soft skillsFINT0049 Science for all : Effective science communication in English Hansel Aude Schutz Natassia 3 12h th. 12h th. FINT0048 Artificial intelligence: challenges and opportunities Frenay Benoît 3 24h th. -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 SMATB318 Introduction to the didactics of mathematics Dubussy Christophe 5 30h th. + 30h ex. -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 SMATB334 Problem solving and mathematical modelling Mauroy Alexandre 5 30h th. + 22.5h ex. SMATB325 Regression models Kiriliouk Anna 5 30h th. + 22.5h ex. -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 Soft skillsINFOB212 Database Engineering Cleve Anthony 5 30h th. + 7h ex. 15h th. + 8h ex. INFOB313 Analysis and Modelling of Information Systems Heymans Patrick Amrani Moussa 5 30h th. + 30h ex. -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 SBIOB003 Pluridisciplinary scientific field trip Yans Johan Silvestre Frédéric Yans Johan Silvestre Frédéric 3 48h th. + 48h ex. SGOGB314 Climatology Houssiau Laurent 5 30h th. + 40h ex. SGOLB313_P33839 Geophysics Louette Pierre Collinet Max 3 15h th. + 15h ex. SCHIB309 Mathematical chemistry Champagne Benoît 5 30h th. + 22.5h ex. -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 ECGEB375 International economic relations De Crombrugghe De Picquendaele Alain 5 30h th. + 15h ex. ECGEB383 Finance Giot Pierre SOUDANT Joey 5 45h th. + 15h ex. -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 SMATB392 Student researcher project Q1-Q2 Henry Valérie 10 SMATB390 Student-researcher" project Q2 Henry Valérie 5 SMATB391 Student-researcher" project Q1 Henry Valérie 5
-
Les métiers des mathématiciens
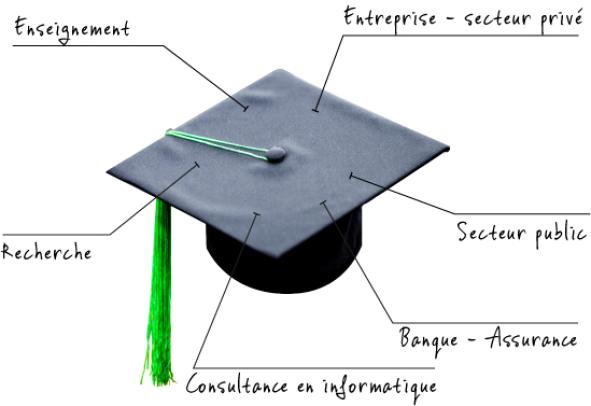
Careers in mathematics
For graduates in applied mathematics from the University of Namur, the transition from studies to the world of work presents no major difficulties: schools are short of mathematics teachers; the business world is looking for skills in networks, dynamic systems, optimization, control, modeling and programming, all assets that mathematicians trained at UNamur possess.
Confronting mathematics with reality
Many mathematicians invest their knowledge within companies. Many business sectors appreciate their analytical and synthesizing skills, as well as their rigor. Whether in consultancy or in the economic and industrial world, mathematicians have plenty of room to model phenomena and situations and, more broadly, put their mathematical baggage at the service of society.
Building IT solutions
Mathematicians at UNamur receive a solid training in scientific programming, an asset that many of them put to good use within various organizations (private or public), or in IT service companies. After a few years in applications development, mathematicians generally move on to project management.
Whatever their job title and level of responsibility, they work to bring human beings and an information management and processing system into harmonious interaction... an ongoing challenge that demands a good sense of interpersonal relations and an excellent knowledge of technology and the business world.
My job as an IT manager is at times akin to a mathematical demonstration. I start with a hypothesis, i.e. the existing situation, the budget, the resources, and I have to arrive at a thesis, in this case a major business project, such as setting up a company abroad. To achieve this, I conduct a real demonstration using lemmas, i.e. small implementations of IT solutions. To set up a company abroad, for example, you need to secure your IT network.
Alain Dieudonné, IT Manager
Evaluating financial or economic risks
Risk management is a strategic issue in banking and financial organizations, stock markets, insurance companies, but also parastatal institutions for social security, pension control, etc. Thanks to their sound knowledge of modeling, mathematicians often perform functions linked to controlling the uncertainty inherent in most economic activities.
Producing statistics
Statistics play an important role in today's society: opinion polls and surveys are part of our daily lives. Some consultancies specializing in conducting this type of analysis call on mathematicians.
Modeling reality
Whether it's the shape of contact lenses, the dynamics of a population, the concentration of space debris, the movements of the oceans, the understanding of social networks, the work of mathematicians is always linked to modeling: being able to understand, simplify, conceptualize and visualize a situation, to come out with a more abstract model likely to provide a global description of a phenomenon.
I've been working for a few years as an actuary in a consultancy firm in the field of supplementary pensions. We live in a world full of hazards: the actuary's role is to quantify, to model uncertainties... Above all, mathematics enables us to develop our way of thinking, which makes our capacity for analysis our main working tool.
Noémie Laloux, actuary
Transmitting a passion for reality
Teaching and the world of training still represent one of the major outlets for mathematicians. Almost a third of our young, professionally active graduates communicate their passion for the real world by teaching mathematics and/or science in upper secondary schools, colleges and universities.
The subject we teach is not particularly difficult. Above all, we need to give young people a taste for mathematics and help those with difficulties to understand it. It's a daily challenge.
Marie Matelart, Secondary school mathematics teacher
Pushing the limits of our knowledge
Mathematicians pursue research mainly in academic settings, in Belgium or abroad. Universities and public funds (FNRS, FRIA, etc.) finance the completion of a PhD (between 4 and 6 years) or award time-limited grants for participation in a research program, sometimes in partnership with the business world.
Aside from fundamental research, mathematics is often a valuable tool for scientific progress in other disciplines: computer science, astrophysics and physics, meteorology, economics, transport, biology... In these multidisciplinary contexts, dual skills often represent an asset.
