Bachelor in Biomedical Sciences
-
Schedule
regular course
- ECTS Credits 180

During the bachelor's degree, you learn to master the fundamentals of physics, chemistry, and biology on which the teaching of biomedical sciences is based.
Through a morphological approach (cytology, histology, anatomy and embryology), you learn to identify and describe the main structures and functions of intracellular organelles, the various cell types, and the anatomical tissues and structures that make up the human body.
You study the normal functioning of the human body as well as the pathophysiology of major human diseases (biochemistry, genetics, microbiology, physiology, neuroscience, psychology, immunopathology, pathology...).
In parallel, you will learn about cutting-edge technologies in biomedical research (courses in methodology, instrumental analysis and radiation protection, model organisms...), therapeutic perspectives (innovative therapy, molecular diagnostics, pharmacology, clinical development), as well as ethics.

You're off to a good start
- you're open to scientific problems;
- you're rigorous and precise;
- you're able to synthesize;
- you're able to decompartmentalize disciplines to establish links between their content.
Teaching methods
Courses, seminars, practical work, exercise sessions and laboratories, everything is done to ensure that you master the theoretical concepts.
Organized in small groups, practical work and exercise sessions introduce you to the techniques specific to each discipline.
You learn how to use the equipment, take measurements and then interpret them. In this way, you observe, experimentally, certain laws or phenomena exposed in the theoretical lessons. You learn to recognize and represent the cells or organisms observed under the optical microscope, but also to reconstitute them in space.
Significant resources are devoted to your introduction to microscopic practice: collection of microscopic sections of human specimens, binocular microscopes, electron micrographs, multimedia learning system...
In addition to the many practical sessions in microscopy, biochemistry, microbiology, genetics... you can apply to become a "student-researcher" during your bachelor's degree. This status enables you to join a Faculty laboratory and learn the profession of researcher, working hand-in-hand with professionals in the biomedical sciences. You work on a research project, discover cutting-edge technologies, and develop your scientific approach.
Success aids
Succeeding in a year of study at university involves many challenges.
To help you meet them, we support you in developing your disciplinary, methodological and human skills... with the support of numerous professionals.
Preparatory courses, individualized help...
Training with an international outlook
As part of the bachelor's program, you have the opportunity to study abroad for a semester.
The destinations are varied, both in Europe (France, Spain, Sweden...) and outside Europe (USA, Canada...).
During this semester, you'll have the opportunity to continue your studies while discovering a region, a culture, a country. This great experience will enable you to gain independence, develop your employability skills, and possibly learn a foreign language.
Opportunities for training abroad continue in the master's program.
After the baccalauréat
As bachelor graduates in biomedical sciences, you can access the programs of:
- Master 120 in Biomedical Sciences
- Master 60 in Biomedical Sciences
- International Master in Translational Cosmetic and Dermatological Sciences (EMOTION)
- Master 120 in Biochemistry and Molecular and Cellular Biology
- Master 60 en Sciences Biologiques
- Master in Molecular Microbiology
organized at UNamur.
-
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Th.+Ex. Credits/Block 1 2 3 SPHYB161 Life Science Physics I: Mechanics Louette Pierre 45h th. + 22.5h ex. 6 SPHYB162 Life Science Physics II: Electricity, Magnetism and Nuclear Louette Pierre 40h th. + 12.5h ex. 5 SPHYB163 Life science physics III: waves, sound, optics Louette Pierre 20h th. + 10h ex. 3 SMATB111 Mathematics Daquin Jérôme 30h th. + 15h ex. 3 MMEDB283 Introduction to medical statistics Bihin Benoît Bihin Benoît 24h th. + 15h ex. 4 SCHIB111 General chemistry Wouters Johan 50h th. + 24h ex. 7 SCHIB112 General solution chemistry Dehon Jérémy 25h th. + 16h ex. 4 MCHIB107 Organic Chemistry Lanners Steve 45h th. + 35h ex. 7 -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Th.+Ex. Credits/Block 1 2 3 MBIMB304 Introduction to bibliographic research and the critical presentation of its results Canon Caroline Hennequart Marc 5 -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Th.+Ex. Credits/Block 1 2 3 SVETB112 Cytology Boonen Marielle 20h th. 2 MMEDB253 Embryology Maystadt Isabelle 26h th. 3 MMEDB113 Histology II Nicaise Charles Balligand Thomas 39h th. + 20h ex. 5 MMEDB214 Biomedical Anatomy I and II Garin Pierre 45h th. 6 MMEDB226 Histology I Nicaise Charles 25h th. + 20h ex. 4 -
<unknown>
-
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Th.+Ex. Credits/Block 1 2 3 MBIMB305 Introduction to clinical development Beaudart Charlotte 15h th. 2 MBIMB306 Innovative therapy: medical devices Nolens Grégory 20h th. + 5h ex. 3 MBIMB308 Molecular diagnosis Karadurmus Deniz 22h th. 3 MMEDB334 Elements of general pharmacology Gillet Jean-Pierre 24h th. + 8h ex. 4 -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Th.+Ex. Credits/Block 1 2 3 MMEDB211 Introduction to analytic equipment methodology in biomedical sciences Nisolle Jean-François Arnould Thierry HEUSKIN Anne-Catherine 24h th. 4 MMEDB220_P34566 Partim Medical epidemiology Roberfroid Dominique 18h th. + 10h ex. 2 MBIMB301 Ultracentrifugation Boonen Marielle 15h th. + 5h ex. 2 MMEDB352 Basic methods in cell and tissue biology Lambert De Rouvroit Catherine 20h th. + 45h ex. 4 MMEDB344 Hot topics in preclinical and clinical research Boonen Marielle Hennequart Marc Gillet Jean-Pierre Beaudart Charlotte 22h th. 2
-
-
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Th.+Ex. Credits/Block 1 2 3 MSPSB142 Philosophy of biomedicine Pontarotti Gaëlle LAURENT Nathanaël 20h th. + 15h ex. 3 MSPSB140 Religious Studies Malvaux Paul 30h th. 3 Soft skillsMMEDB272_P35277 <unknown> Desseilles Martin 26h th. 3 MBIMB303 Bioethics Ravez Laurent 30h th. 2 -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Th.+Ex. Credits/Block 1 2 3 MELVB104 Introduction to scientific English (level B1 and above) Hansel Aude 30h th. 2 MELVB204 English for biomedical students (level B1+ and above) Zimmer Carole 30h th. 2 Soft skillsMELVB300 English communication skills for biomedical students (level B2 and above) Zimmer Carole 30h th. 2
-
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 SPHYB161 Life Science Physics I: Mechanics Louette Pierre 6 45h th. + 22.5h ex. SPHYB162 Life Science Physics II: Electricity, Magnetism and Nuclear Louette Pierre 5 40h th. + 12.5h ex. SPHYB163 Life science physics III: waves, sound, optics Louette Pierre 3 20h th. + 10h ex. SMATB111 Mathematics Daquin Jérôme 3 30h th. + 15h ex. SCHIB111 General chemistry Wouters Johan 7 50h th. + 24h ex. SCHIB112 General solution chemistry Dehon Jérémy 4 25h th. + 16h ex. MCHIB107 Organic Chemistry Lanners Steve 7 45h th. + 35h ex. -
<unknown>
-
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 SVETB112 Cytology Boonen Marielle 2 20h th. -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 SBIOB153 Biology of organisms Renard Henri-François 4 35h th. SBIOB154 Practical application of organismal biology Renard Henri-François 2 20h ex. MBIMB109 Genetics Maystadt Isabelle De Backer Olivier 6 52h th. + 17h ex. SBIOB157 General biology Messiaen Johan 6 35h th. + 22h ex.
-
-
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 MSPSB142 Philosophy of biomedicine Pontarotti Gaëlle LAURENT Nathanaël 3 20h th. + 15h ex. -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 MELVB104 Introduction to scientific English (level B1 and above) Hansel Aude 2 15h th. 15h th.
-
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 MMEDB283 Introduction to medical statistics Bihin Benoît Bihin Benoît 4 24h th. + 15h ex. -
<unknown>
-
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 MMEDB253 Embryology Maystadt Isabelle 3 26h th. MMEDB113 Histology II Nicaise Charles Balligand Thomas 5 39h th. + 20h ex. MMEDB214 Biomedical Anatomy I and II Garin Pierre 6 45h th. MMEDB226 Histology I Nicaise Charles 4 25h th. + 20h ex. -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 MBIMB201 Molecular genetics and genomics De Backer Olivier 5 30h th. + 30h ex. MPHAB202 General biochemistry Masereel Bernard 5 45h th. Soft skillsMPHAB203 Experimental biochemistry Masereel Bernard 3 25h ex. MMEDB222 General physiology Kirschvink Nathalie 6 41h th. + 15h ex. MMEDB205 General Immunology Graux Carlos 3 26h th. MBIOB262 General microbiology Lambert De Rouvroit Catherine 2 15h th. -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 MMEDB211 Introduction to analytic equipment methodology in biomedical sciences Nisolle Jean-François Arnould Thierry HEUSKIN Anne-Catherine 4 24h th. MMEDB220_P34566 Partim Medical epidemiology Roberfroid Dominique 2 18h th. + 10h ex.
-
-
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 MSPSB140 Religious Studies Malvaux Paul 3 30h th. Soft skillsMMEDB272_P35277 <unknown> Desseilles Martin 3 26h th. -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 MELVB204 English for biomedical students (level B1+ and above) Zimmer Carole 2 15h th. 15h th.
-
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 MBIMB304 Introduction to bibliographic research and the critical presentation of its results Canon Caroline Hennequart Marc 5 -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 MBIMB307 Cellular pathobiology Hamer Isabelle 2 20h th. MMEDB308 Immunopathology Graux Carlos 2 13h th. MPHAB306 Human biochemistry Dogne Jean-Michel SIRIEZ Romain 6 60h th. MMEDB356 General pathology Gourdin Maximilien 4 30h th. + 15h ex. MBIOB361 Medical microbiology Tré-Hardy Marie 4 30h th. + 12h ex. MMEDB331 Human Physiology Kirschvink Nathalie 6 60h th. + 20h ex. MBIMB302 Cell growth, differentiation and death Michiels Carine Balligand Thomas 3 30h th. MBIMB300 Neuroscience Desseilles Martin De Backer Olivier 4 45h th. -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 MBIMB305 Introduction to clinical development Beaudart Charlotte 2 15h th. MBIMB306 Innovative therapy: medical devices Nolens Grégory 3 20h th. + 5h ex. MBIMB308 Molecular diagnosis Karadurmus Deniz 3 22h th. MMEDB334 Elements of general pharmacology Gillet Jean-Pierre 4 24h th. + 8h ex. -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 MBIMB301 Ultracentrifugation Boonen Marielle 2 15h th. + 5h ex. MMEDB352 Basic methods in cell and tissue biology Lambert De Rouvroit Catherine 4 20h th. + 45h ex. MMEDB344 Hot topics in preclinical and clinical research Boonen Marielle Hennequart Marc Gillet Jean-Pierre Beaudart Charlotte 2 22h th.
-
-
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 MBIMB303 Bioethics Ravez Laurent 2 30h th. -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 Soft skillsMELVB300 English communication skills for biomedical students (level B2 and above) Zimmer Carole 2 15h th. 15h th.
Jury
Les métiers des sciences biomédicales
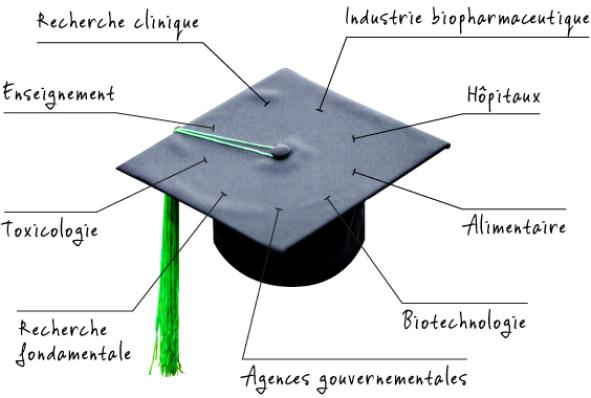
Careers in biomedical sciences
Advancing research in the field of human health
The biomedical sciences open the door to many professional opportunities, mainly in the field of research, whether basic or applied, in universities, industry, teaching hospitals or government agencies.
Biomedical basic research aims to understand, through an experimental approach, how the human being functions at the cellular and molecular level. The answers it provides may one day find clinical applications.
Applied biomedical research puts the findings of basic research into practice. Its aim is to improve diagnostic and therapeutic methods. It may, for example, be aimed at the design of new vaccines, new diagnostic tests...
Clinical research is a side of applied research that consists of improving diagnostic and therapeutic methods based on data present in patients' medical records.
Alongside research, the clinical field offers many professional orientations: toxicology, nutrition, clinical biology, bioengineering, medical imaging...
I'm doing a PhD thesis in toxicology. I'm trying to understand esophageal cancer and find new targets for a therapy against this disease. I recently presented the state of my research at a conference in California.
Céline, PhD student in toxicology
Serving the pharmaceutical and biotech industry
The world of industry is not limited to research: some biomedical scientists pursue careers in drug production, quality control, medical delegation as well as regulatory affairs.
Graduates in biomedical sciences can choose to specialize in biostatistics right from the Master's level. In this way, they acquire a profile in demand by companies active in life science fields that require the processing of quantitative data (e.g. epidemiology or clinical studies).
As a clinical research assistant, I administratively manage and coordinate clinical studies, for example in anti-cancer treatments, conducted by pharmaceutical industries, international organizations or groups of physicians. I check that protocols are handled with strict respect for patients, procedures and study objectives. My colleagues and I evaluate the efficacy and tolerance of the various treatments. In addition to these tasks, we occasionally attend investigative meetings abroad in preparation for a new study at our center.
Anne-Laure, Clinical Research Assistant
Sharing and disseminating scientific advances
Thanks to training that considers the human applications of research, biomedical scientists can promote science as a real-world discipline, for example in the education sector (graduates have access to the agrégation de l'enseignement secondaire supérieur). They can also advise governmental or parastatal bodies, particularly in the field of public health.
Provided they are sensitive to development issues, they are also apt to manage biomedical projects in developing countries.
I visit university centers to inform Key Opinion Leaders about our cardiology and gynecology products. I also negotiate contracts allowing our products to appear on hospital formularies and organize regular scientific meetings.
Christian, Product specialist in the pharmaceutical industry