Bachelor in Pharmacy
-
Schedule
regular course
- ECTS Credits 180

To gain a perfect understanding of drugs and their effects on living organisms, and particularly on humans, you will learn to master the physical, chemical and biological processes essential to the pharmaceutical approach.
Pharmaceutical specificity (pharmaceutical chemistry, studies of active substances derived from plants, study of the interaction of therapeutic substances with the human organism...) quickly takes a predominant place in your training, as does the handling of laboratory and analysis equipment.
Throughout your course, you acquire in-depth knowledge of diseases and therapeutic strategies, and learn to manage the human dimension of the pharmacist-patient relationship.
Scientific training takes ethical aspects into account, enabling you to play a major role as public health advisors to help improve our health and quality of life.

You're off to a good start
- you are able to demonstrate rigor, order and precision;
- you are observant;
- you have real people skills;
- you have a good scientific grounding (mathematics, physics, chemistry, biology).
Teaching methods
Scientific concepts are taken from their starting point, but the presentation is fairly quick on concepts that are part of the secondary school curriculum.
Theory, seminars, laboratories and exercise sessions, everything is done to ensure that you master
the concepts.
Organized in small groups, laboratories and exercise sessions introduce you to techniques specific to each discipline. Interactive boards, forums, online questionnaires... are available to make it as easy as possible for you to keep in touch with your teachers.
The pharmaceutical sciences sector allows you to combine the scientific and human aspects. By becoming specialists in medicines, we ensure their proper use and the safety of patients.
Behind every drug lies a complex development process and a perpetual questioning process offering young graduates numerous career prospects.
In addition, the campus of the University of Namur is very pleasant and the reputation of the teaching conditions reinforced my choice. The professors are approachable and the training lives up to my expectations."
Laure, assistant

Success aids
Succeeding in a year of study at university involves many challenges.
To help you meet them, UNamur supports you in developing your disciplinary, methodological and human skills... with the support of numerous professionals.
Preparatory courses, individualized help...
After the baccalauréat: the master's degree

The University of Namur is organizing:
- Master 120 in Pharmaceutical Sciences
- Master 120 in Biomedical Sciences
- Master 60 in Biomedical Sciences
directly accessible after obtaining your bachelor's degree in pharmaceutical sciences.
-
<unknown>
-
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Th.+Ex. Credits/Block 1 2 3 SPHYB161 Life Science Physics I: Mechanics Louette Pierre 45h th. + 22.5h ex. 6 SPHYB162 Life Science Physics II: Electricity, Magnetism and Nuclear Louette Pierre 40h th. + 12.5h ex. 5 SPHYB163 Life science physics III: waves, sound, optics Louette Pierre 20h th. + 10h ex. 3 SBIOB153 Biology of organisms Renard Henri-François 35h th. 4 SBIOB154_P35329 <unknown> Renard Henri-François 16h ex. 2 SBIOB157 General biology Messiaen Johan 35h th. + 22h ex. 6 SCHIB111 General chemistry Wouters Johan 50h th. + 24h ex. 7 SCHIB112 General solution chemistry Dehon Jérémy 25h th. + 16h ex. 4 MCHIB107 Organic Chemistry Lanners Steve 45h th. + 35h ex. 8 MBIOB200 Botanical introduction to pharmacognosy and mycology Messiaen Johan 30h th. + 15h ex. 4 MPHAB287 Computational methods applied to pharmaceutical sciences BORETTI Emma Douxfils Jonathan 10h ex. 2 MMEDB283 Introduction to medical statistics Bihin Benoît Bihin Benoît 24h th. + 15h ex. 4 -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Th.+Ex. Credits/Block 1 2 3 MSPSB142 Philosophy of biomedicine Pontarotti Gaëlle LAURENT Nathanaël 20h th. + 15h ex. 3 MSPSB140 Religious Studies Malvaux Paul 30h th. 3 Soft skillsMMEDB272_P35277 <unknown> Desseilles Martin 26h th. 3 MMEDB220_P34566 Partim Medical epidemiology Roberfroid Dominique 18h th. + 10h ex. 2 MSPSB328 Medical Bioethics Ravez Laurent 22.5h th. 2 Soft skillsMPHAB397 Pharmacist-patient relationship Desseilles Martin 10h ex. 2 -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Th.+Ex. Credits/Block 1 2 3 MPHAB315 End of cycle work in Pharmaceutical Sciences and observation period in a pharmacy Masereel Bernard SIRIEZ Romain GILLOT Constant 30h ex. 6 -
<unknown>
-
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Th.+Ex. Credits/Block 1 2 3 MMEDB212 Anatomy applied to pharmaceutical sciences, including an introduction to medical imaging Garin Pierre Nisolle Jean-François 35h th. + 2h ex. 4 MMEDB216 Cytology and human histology Balligand Thomas 45h th. + 15h ex. 5 -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Th.+Ex. Credits/Block 1 2 3 MPHAB202 General biochemistry Masereel Bernard 45h th. 5 Soft skillsMPHAB203 Experimental biochemistry Masereel Bernard 25h ex. 3 MMEDB205 General Immunology Graux Carlos 26h th. 3 MBIOB262 General microbiology Lambert De Rouvroit Catherine 15h th. 2 MBIOB215 Génie génétique et éléments de génomique Maystadt Isabelle 22.5h th. 3 MPHAB306 Human biochemistry Dogne Jean-Michel SIRIEZ Romain 60h th. 6 MMEDB331 Human Physiology Kirschvink Nathalie 60h th. + 20h ex. 6 MMEDB222 General physiology Kirschvink Nathalie 41h th. + 15h ex. 6
-
-
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Th.+Ex. Credits/Block 1 2 3 MELVB103 Introduction to scientific English (level B1 and above) Bar Vanina 30h th. 3 MELVB203 English : communicating science effectively (level B1+ or higher) Bouchat Hélène 30h th. 3 -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Th.+Ex. Credits/Block 1 2 3 SBIOB003 Pluridisciplinary scientific field trip Yans Johan Silvestre Frédéric Yans Johan Silvestre Frédéric 48h th. + 48h ex. 3 3
-
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 MPHAB100 Introduction to pharmaceutical sciences Masereel Bernard 6 30h th. + 10h ex. -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 SPHYB161 Life Science Physics I: Mechanics Louette Pierre 6 45h th. + 22.5h ex. SPHYB162 Life Science Physics II: Electricity, Magnetism and Nuclear Louette Pierre 5 40h th. + 12.5h ex. SPHYB163 Life science physics III: waves, sound, optics Louette Pierre 3 20h th. + 10h ex. SBIOB153 Biology of organisms Renard Henri-François 4 35h th. SBIOB154_P35329 <unknown> Renard Henri-François 2 16h ex. SBIOB157 General biology Messiaen Johan 6 35h th. + 22h ex. SCHIB111 General chemistry Wouters Johan 7 50h th. + 24h ex. SCHIB112 General solution chemistry Dehon Jérémy 4 25h th. + 16h ex. MCHIB107 Organic Chemistry Lanners Steve 8 45h th. + 35h ex. -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 MSPSB142 Philosophy of biomedicine Pontarotti Gaëlle LAURENT Nathanaël 3 20h th. + 15h ex. MSPSB140 Religious Studies Malvaux Paul 3 30h th. -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 MELVB103 Introduction to scientific English (level B1 and above) Bar Vanina 3 15h th. 15h th.
-
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 MPHAB286 Molecular structure and properties Pochet Lionel 4 25h th. + 10h ex. MPHAB288 Pharmacology - pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic approach, including alternative methods to animal testing Douxfils Jonathan Douxfils Jonathan 5 40h th. MPHAB284 Introduction to pharmaceutical analysis Pochet Lionel 4 25h th. + 30h ex. MPHAB285 Medicinal Chemistry: introduction Dogne Jean-Michel 5 20h th. -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 MBIOB200 Botanical introduction to pharmacognosy and mycology Messiaen Johan 4 30h th. + 15h ex. MPHAB287 Computational methods applied to pharmaceutical sciences BORETTI Emma Douxfils Jonathan 2 10h ex. MMEDB283 Introduction to medical statistics Bihin Benoît Bihin Benoît 4 24h th. + 15h ex. -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 Soft skillsMMEDB272_P35277 <unknown> Desseilles Martin 3 26h th. -
<unknown>
-
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 MMEDB212 Anatomy applied to pharmaceutical sciences, including an introduction to medical imaging Garin Pierre Nisolle Jean-François 4 35h th. + 2h ex. MMEDB216 Cytology and human histology Balligand Thomas 5 45h th. + 15h ex. -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 MPHAB202 General biochemistry Masereel Bernard 5 45h th. Soft skillsMPHAB203 Experimental biochemistry Masereel Bernard 3 25h ex. MBIOB215 Génie génétique et éléments de génomique Maystadt Isabelle 3 22.5h th. MMEDB222 General physiology Kirschvink Nathalie 6 41h th. + 15h ex.
-
-
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 MELVB203 English : communicating science effectively (level B1+ or higher) Bouchat Hélène 3 15h th. 15h th. -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 SBIOB003 Pluridisciplinary scientific field trip Yans Johan Silvestre Frédéric Yans Johan Silvestre Frédéric 3 48h th. + 48h ex.
-
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 MPHAB312 Pharmacognosy - Part II: Therapeutic activity of plants Douxfils Jonathan GILLOT Constant 4 30h th. + 20h ex. MPHAB314 Pharmaceutical chemistry - Part II Dogne Jean-Michel 4 30h th. MPHAB316 Integrated practical work in Pharmaceutical Sciences GILLOT Constant DJOKOTO Happy 6 60h ex. MPHAB313 Pharmaceutical chemistry - Part I Dogne Jean-Michel 2 20h th. MPHAB309 Pharmaceutical analysis - Part II Pochet Lionel 4 25h th. + 20h ex. MPHAB310 Pharmacognosy - Part I: Phytochemistry Douxfils Jonathan 3 20h th. MPHAB311 Introduction to galenics Douxfils Jonathan 3 20h th. MPHAB333 Pharmacology - pathophysiological and systematic approach Musuamba Tshinanu Flora Douxfils Jonathan GILLOT Constant 5 55h th. + 10h ex. -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 MMEDB220_P34566 Partim Medical epidemiology Roberfroid Dominique 2 18h th. + 10h ex. MSPSB328 Medical Bioethics Ravez Laurent 2 22.5h th. Soft skillsMPHAB397 Pharmacist-patient relationship Desseilles Martin 2 10h ex. -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 MPHAB315 End of cycle work in Pharmaceutical Sciences and observation period in a pharmacy Masereel Bernard SIRIEZ Romain GILLOT Constant 6 30h ex. -
<unknown>
-
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 MMEDB205 General Immunology Graux Carlos 3 26h th. MBIOB262 General microbiology Lambert De Rouvroit Catherine 2 15h th. MPHAB306 Human biochemistry Dogne Jean-Michel SIRIEZ Romain 6 60h th. MMEDB331 Human Physiology Kirschvink Nathalie 6 60h th. + 20h ex.
-
-
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 SBIOB003 Pluridisciplinary scientific field trip Yans Johan Silvestre Frédéric Yans Johan Silvestre Frédéric 3 48h th. + 48h ex.
Les métiers des pharmaciens
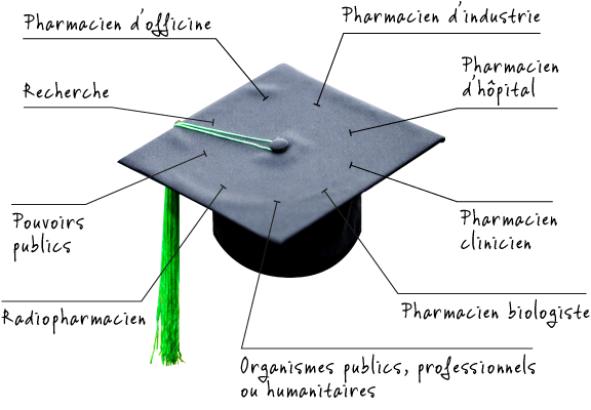
Pharmacists' professions
The dispensary is the traditional sector for pharmacists. In the past, all pharmacists' roles were centralized here. Preparing medicines in accordance with a doctor's prescription, they made "magistral preparations" - tablets, pills, syrups - from substances of biological or mineral origin, most of which were themselves prepared and analyzed in the dispensary. They dispensed their own preparations to patients, for which they bore, de facto, full responsibility.
Scientific and social developments, in particular the emergence of the pharmaceutical speciality, have changed the predominance of these roles. Adapting to this new situation means that, faced with an ever more complex and diversified therapeutic arsenal, the overriding role of pharmacists today is to have perfect knowledge of the drugs they dispense and their effects. More than ever, they are the last line of defence between the drug and the patient, whom they must be able to guide and advise on its use.
About 70% of graduates go on to become officine pharmacists. Twice as frequently consulted as doctors, and enjoying enormous trust capital among the population, dispensing pharmacists are front-line public health players. Their role as advisors in the dispensing of medicines, pharmaceutical follow-up and patient support is essential. To fulfill this task, it's important to have a sound knowledge of medicines and the various pathologies, and to be a good listener and communicator.
Pharmacists can also play an important role in a wide variety of other areas that are difficult to list. For example, pharmacists are active in toxicology, hygiene and environmental protection, food analysis, cosmetology, dietetics, phytotherapy, etc., as well as in research and higher education.
In the pharmaceutical industry, industrial pharmacists have their place in research and development (drug development, galenics, analysis...), contribute to clinical studies, are involved in regulatory affairs concerning, among other things, drug registration, are responsible for drug production, control (QC) and quality assurance (QA). Finally, certain key positions must be filled by industrial pharmacists.
In the hospital environment, hospital pharmacists manage and lead the pharmaceutical department. They are responsible for the manufacture, control, analysis, sterilization, and dispensing of medicines, as well as managing the hospital pharmacy. Specialists in drugs and medical equipment (prostheses, surgical equipment...), they are in constant contact with nursing staff (doctors, nurses...).
In hospitals, clinical pharmacists are part of the healthcare team. Also in contact with patients, their aim is to optimize drug use (rational choice, adverse effects, cost...).
Pharmacist-biologists manage the clinical biology (or medical analysis) laboratory, either private or attached to hospitals. They are responsible not only for the quality of analyses, but also for their interpretation. In collaboration with physicians, they contribute to the diagnosis of disease through the information they provide. Clinical biology comprises three main fields: medicinal chemistry (analysis of chemical and biochemical components, toxicology, etc.), hematology (analysis of blood cells and proteins, immunology, etc.) and microbiology (analysis of bacteria, viruses, parasites, etc.).
Radiopharmacists, meanwhile, are responsible for the production and control of radioisotopes for diagnostic (medical imaging) and therapeutic (radiotherapy) use.
A number of administrations and organizations call on the skills of pharmacists. These include public authorities (e.g. Federal Agency for Medicines and Health Products, which organizes the Pharmacy Inspectorate), the army (Health Service), public bodies (INAMI, mutual insurance companies), professional organizations (Belgian Pharmaceutical Association, Drug Control Service...) or humanitarian organizations (Pharmacists without Borders).