Bachelor in Biology
-
Schedule
regular course
- ECTS Credits 180

The Bachelor's program in biology at the University of Namur is characterized by a study, right from the start, of the major fields of biology (cellular and molecular biology, plant, animal and microorganism diversity and evolution, evolutionary theories, histology).
The training is rounded out with fundamental notions of chemistry and experimental physics, as well as statistics and programming.
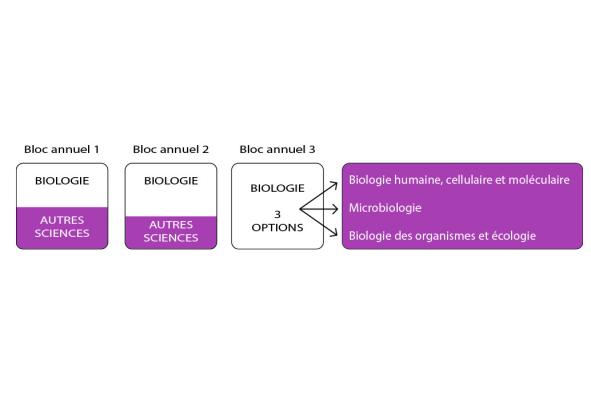
Thereafter, biology training intensifies and specializes with courses in physiology, genetics, biochemistry, microbiology, ecology and bioinformatics.
In the third block, you customize your training by choosing an option. This option doesn't close any doors for you, either in the master's program or on the job market.
You develop a good knowledge of English to understand scientific literature, but also to exchange with other scientists in your field (some courses are given in English immersion).
A human dimension completes your bachelor's degree with a reflective approach to the role and impact of science in society.
You're off to a good start
- you're passionate about living things and curious to learn how living organisms and processes work;
- you feel at home in biology, physics, chemistry and mathematics, without necessarily having followed a strong program in high school;
- you have an analytical and synthesizing mind;
- You're motivated by the idea of learning English and being able to communicate in this language.
Teaching methods
Courses, seminars, practical work, exercise sessions, laboratories, internships... everything is done to ensure excellent mastery of concepts and the development of practical skills in the techniques most commonly used by biologists.
Organized in small groups, practical work and exercise sessions introduce you to the techniques specific to each discipline. You'll learn how to use the equipment, make measurements and then interpret them. In this way, you observe, experimentally, certain laws or phenomena exposed in the theoretical lessons.
Excursions and internships are essential for a natural science like biology. That's why, in addition to exercises and laboratories, you'll take part in real-life days putting your discipline to work: marine biology and ecology internships, environmental biology internships, ecology and integrative biology internships, multidisciplinary summer internships, or immersion internships in laboratories, industry and hospitals.
Independence and critical thinking are skills you learn to develop throughout your training. For example, during "flipped classrooms" or problem-based learning, you prepare parts of the material in groups supervised by a teacher. You present your findings and formulate questions to make the most of the interaction with the teacher.
Thanks to the "student-researcher" project, you can learn about research under the supervision of a departmental researcher. This experience also enables you to develop your autonomy, creativity and critical thinking skills.
If you choose the Block 3 "Biology Tutorial", you'll be able to supervise Block 1 and 2 students during practical work, and so get your first teaching experience.
The completion of an end-of-cycle project on a topic of your choice closes your bachelor's degree. This project is handled bibliographically, pedagogically (to enable you to take part in a science dissemination activity) or experimentally (accompanying a researcher to the laboratory).

A program rooted in sustainable development
Lethal viruses, chronic diseases, loss of biodiversity, global warming, food resources... are complex societal issues involving life in all its forms.
Analyze the intimate components of these problems and develop solutions for the future!
Success aids
Succeeding in a year of study at university involves many challenges.
To help you meet them, UNamur supports you in developing your disciplinary, methodological and human skills... with the support of numerous professionals.
Preparatory courses, individualized help... Discover the schemes set up for your training.
After the baccalauréat: the master's degree
The University of Namur organizes
- the master in biochemistry and molecular and cellular biology
- the master in organismal biology and ecology, à finalité approfondie
- the master in molecular microbiology
- the master 60 in biological sciences
directly accessible after obtaining a bachelor's degree in biological sciences.
-
<unknown>
-
<unknown>
-
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Th.+Ex. Credits/Block 1 2 3 SBIOB327 Genetic and epigenetic regulations Poncin Katy FINET Olivier Yague-Sanz Carlo 30h th. 2 SVETB313 Applied microbiology Gillet Nicolas 20h th. 2 SBIOB355 Introduction to omics analysis Renard Patricia Arnould Thierry De Bolle Xavier 15h th. + 15h ex. 2 SBIOB310 Techniques in Biochemistry Arnould Thierry 15h th. + 27h ex. 2 SBIOB301 Molecular Mechanisms of Development Renard Patricia Messiaen Johan Matroule Jean-Yves 24h th. 2 SMEDB358 Integrated and biological approach to diseases Gourdin Maximilien Pierson Audrey Lambert De Rouvroit Catherine Desseilles Martin 30h th. + 15h ex. 2 SBIOB345 Human cell biology Renard Henri-François 15h th. + 10h ex. 2 SBIOB344 Visits to laboratories, industry and hospitals Renard Henri-François 20h ex. 2 SBIOB332 Mechanisms of cell responses to stimuli Michiels Carine Renard Patricia 15h th. + 10h ex. 2 -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Th.+Ex. Credits/Block 1 2 3 SBIOB343 Conservation and Population Genetics Dennis Alice 14h th. + 10h ex. 2 SBIOB003 Pluridisciplinary scientific field trip Yans Johan Silvestre Frédéric Yans Johan Silvestre Frédéric 48h th. + 48h ex. 3 3 SBIOB367_P36774 <unknown> Thoré Eli Dennis Alice Kestemont Patrick 24h th. + 15h ex. 3 SBIOB368 Applied ecology Kestemont Patrick De Laender Frédérik 20h th. + 15h ex. 4 SBIOB346 Biodiversity and invasive species De Laender Frédérik De Laender Frédérik Marescaux Jonathan 15h th. + 15h ex. 2 SBIOB347 Introduction to ecotoxicology Silvestre Frédéric Thoré Eli Kestemont Patrick 15h th. + 15h ex. 2 SBIOB349 Environmental biology course (including ornithology) Pigneur Lise-Marie 20h ex. 2 SBIOB362 Ecoethology Thoré Eli 24h th. + 15h ex. 3 -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Th.+Ex. Credits/Block 1 2 3 SBIOB372 Immunology of infection Muraille Éric 15h th. 2 SBIOB369 Metabolic diversity and ecology of microorganisms Lima Mendez Gipsi 22h th. + 22h ex. 3 SBIOB375 Internship rotations Hallez Régis De Bolle Xavier Matroule Jean-Yves Renzi Francesco Lima Mendez Gipsi 40h th. 5 SBIOB371 Bacterial pathogenesis De Bolle Xavier Renzi Francesco 15h th. 2 SVETB313 Applied microbiology Gillet Nicolas 20h th. 2 SBIOB370 Bacterial models Matroule Jean-Yves Matroule Jean-Yves 15h th. + 30h ex. 2 SBIOB327 Genetic and epigenetic regulations Poncin Katy FINET Olivier Yague-Sanz Carlo 30h th. 2
-
-
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Th.+Ex. Credits/Block 1 2 3 FINT0043 Global change and the Anthropocene Yans Johan Dendoncker Nicolas Houssiau Laurent Linard Catherine Henry Sabine Poulain Amael Yans Johan 24h th. 3 SBIOB003 Pluridisciplinary scientific field trip Yans Johan Silvestre Frédéric Yans Johan Silvestre Frédéric 48h th. + 48h ex. 3 3 SBIOB350 Tutoring in biology Silvestre Frédéric 24h ex. 3 Soft skillsFINT0049 Science for all : Effective science communication in English Hansel Aude Schutz Natassia 24h th. 3 FINT0048 Artificial intelligence: challenges and opportunities Frenay Benoît 24h th. 3 Soft skillsSBIOB002 Professional observation internship Silvestre Frédéric 3 -
<unknown>
-
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Th.+Ex. Credits/Block 1 2 3 SBIOB208 Marine biology and ecology course Dennis Alice Silvestre Frédéric Silvestre Frédéric Dennis Alice 40h th. + 40h ex. 3 SBIOB309 Ecology course Kestemont Patrick 60h ex. 3 -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Th.+Ex. Credits/Block 1 2 3 SBIOB003 Pluridisciplinary scientific field trip Yans Johan Silvestre Frédéric Yans Johan Silvestre Frédéric 48h th. + 48h ex. 3 3 SVETB343 Internship at the Centre de Recherches Ovines 1 PETIT Astrid 20h ex. 1 SVETB297 Zootechnics course 1 Muylkens Benoît 10h th. 2
-
-
-
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Th.+Ex. Credits/Block 1 2 3 SGOLB102 Introduction to geology Collinet Max 20h th. + 20h ex. 3 SCHIB118 General Chemistry I Ravet Isabelle 60h th. + 20h ex. 7 SCHIB119 General Chemistry II Ravet Isabelle 30h th. + 25h ex. 4 SPHYB113 Syllabus, webcampus, Teams. Colaux Julien 25h th. + 11h ex. 3 SPHYB114 Physics III - Optics Colaux Julien 25h th. + 10h ex. 3 SMATB111_P35319 <unknown> Daquin Jérôme 15h th. + 15h ex. 2 SPHYB112_P36533 Physics I : Mechanics and Waves HEUSKIN Anne-Catherine 46h th. + 22h ex. 5 SBIOB205_P36526 <unknown> De Laender Frédérik 24h th. + 22.5h ex. 4 SBIOB324 Advanced statistics in life sciences Lima Mendez Gipsi 36h th. + 24h ex. 5 SCHIB212 Chimie organique Vincent Stéphane 40h th. + 10h ex. 4 SMATB223 Mathematics II De Vleeschouwer Martine 15h th. + 20h ex. 3 SPHYB117 Supplementary physics in life sciences HEUSKIN Anne-Catherine 15h th. 2 -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Th.+Ex. Credits/Block 1 2 3 SBIOB120 Data management in life sciences, basic principles De Laender Frédérik 8h th. + 12h ex. 2 SBIOB220 Advanced data management in life sciences Lima Mendez Gipsi 12h th. + 15h ex. 2 -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Th.+Ex. Credits/Block 1 2 3 SELVB201 English : Communicating Science Effectively (level B2) Schutz Natassia 30h th. 2 Soft skillsSELVB301 Writing and Presenting a Scientific Literature Review (level B2) Hansel Aude Schutz Natassia 30h th. 2 Soft skillsSELVB101 Introduction to Scientific English (level B1 and above) Schutz Natassia 30h th. 2 -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Th.+Ex. Credits/Block 1 2 3 Translated with DeepL.com (free version)SSPSB102 Religious Studies: Anthropology, Metaphysics and Science Leyens Stéphane Cazalis Roland 30h th. 2 2 SSPSB101 Philosophical questions Sartenaer Olivier Modera Astrid 22.5h th. + 7.5h ex. 2 SSPSB203 Psychology Ravez Laurent 22.5h th. 2 2 SSPSB202 History of science Sartenaer Olivier 22.5h th. 2 SSPSB204 Logic and argumentation Sartenaer Olivier Sartenaer Olivier 22.5h th. 3 SSPSB309 Ethical Leyens Stéphane LAURENT Nathanaël 15h th. 2 SSPSB308 Philosophy of science Sartenaer Olivier 15h th. 2 SSPSB307 Formal logic Sartenaer Olivier 15h th. 2
-
<unknown>
-
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 SBIOB131 Introduction to molecular and cell biology Matroule Jean-Yves Renard Henri-François 5 36h th. + 24h ex. SBIOB132 Theories of evolution Dennis Alice 2 12h th. SBIOB113 Microbial diversity and evolution Matroule Jean-Yves 2 12h th. SBIOB119 Histology of cells and tissues Renard Patricia 3 24h th. + 12h ex. SBIOB126 Animal diversity and evolution Silvestre Frédéric 5 30h th. + 24h ex. SBIOB100 Plant diversity and evolution Messiaen Johan 6 36h th. + 30h ex.
-
-
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 SGOLB102 Introduction to geology Collinet Max 3 20h th. + 20h ex. SCHIB118 General Chemistry I Ravet Isabelle 7 60h th. + 20h ex. SCHIB119 General Chemistry II Ravet Isabelle 4 30h th. + 25h ex. SPHYB113 Syllabus, webcampus, Teams. Colaux Julien 3 25h th. + 11h ex. SPHYB114 Physics III - Optics Colaux Julien 3 25h th. + 10h ex. SMATB111_P35319 <unknown> Daquin Jérôme 2 15h th. + 15h ex. SPHYB112_P36533 Physics I : Mechanics and Waves HEUSKIN Anne-Catherine 5 46h th. + 22h ex. SPHYB117 Supplementary physics in life sciences HEUSKIN Anne-Catherine 2 15h th. -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 SBIOB120 Data management in life sciences, basic principles De Laender Frédérik 2 8h th. + 12h ex. -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 Soft skillsSELVB101 Introduction to Scientific English (level B1 and above) Schutz Natassia 2 15h th. 15h th. -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 Translated with DeepL.com (free version)SSPSB102 Religious Studies: Anthropology, Metaphysics and Science Leyens Stéphane Cazalis Roland 2 30h th. SSPSB101 Philosophical questions Sartenaer Olivier Modera Astrid 2 22.5h th. + 7.5h ex. SSPSB203 Psychology Ravez Laurent 2 22.5h th.
-
<unknown>
-
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 Soft skillsSBIOB229 Current issues in biology Arnould Thierry Silvestre Frédéric 3 20h th. SBIOB232 System Histology Renard Patricia 3 15h th. + 20h ex. SBIOB209 Introduction to Bacteriology De Bolle Xavier 2 15h th. + 10h ex. SBIOB221 General ecology Kestemont Patrick 6 40h th. + 25h ex. SVETB218_P34613 <unknown> Thoré Eli Hontoir Fanny Missawi Omayma 3 25h th. + 12h ex. SBIOB214 Animal physiology II Thoré Eli Silvestre Frédéric Dennis Alice 4 32h th. + 12h ex. SBIOB215_P36773 <unknown> Silvestre Frédéric Dennis Alice Flot Jean-François Flot Jean-François 5 30h th. + 30h ex. SBIOB210 General Biochemistry I Michaux Catherine Renard Patricia 5 45h th. + 22.5h ex. SBIOB213 Génétique Matroule Jean-Yves 5 36h th. + 15h ex. SBIOB228 Plant physiology Messiaen Johan 4 30h th. + 15h ex. -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 SBIOB208 Marine biology and ecology course Dennis Alice Silvestre Frédéric Silvestre Frédéric Dennis Alice 3 40h th. + 40h ex. -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 SBIOB003 Pluridisciplinary scientific field trip Yans Johan Silvestre Frédéric Yans Johan Silvestre Frédéric 3 48h th. + 48h ex.
-
-
-
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 SBIOB205_P36526 <unknown> De Laender Frédérik 4 24h th. + 22.5h ex. SCHIB212 Chimie organique Vincent Stéphane 4 40h th. + 10h ex. SMATB223 Mathematics II De Vleeschouwer Martine 3 15h th. + 20h ex. -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 SBIOB220 Advanced data management in life sciences Lima Mendez Gipsi 2 12h th. + 15h ex. -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 SELVB201 English : Communicating Science Effectively (level B2) Schutz Natassia 2 15h th. 15h th. -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 SSPSB203 Psychology Ravez Laurent 2 22.5h th. SSPSB202 History of science Sartenaer Olivier 2 22.5h th. SSPSB204 Logic and argumentation Sartenaer Olivier Sartenaer Olivier 3 22.5h th. Translated with DeepL.com (free version)SSPSB102 Religious Studies: Anthropology, Metaphysics and Science Leyens Stéphane Cazalis Roland 2 30h th.
-
<unknown>
-
<unknown>
-
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 SBIOB327 Genetic and epigenetic regulations 2 30h th. SVETB313 Applied microbiology 2 20h th. SBIOB355 Introduction to omics analysis Renard Patricia Arnould Thierry De Bolle Xavier 2 15h th. + 15h ex. SBIOB310 Techniques in Biochemistry Arnould Thierry 2 15h th. + 27h ex. SBIOB301 Molecular Mechanisms of Development Renard Patricia Messiaen Johan Matroule Jean-Yves 2 24h th. SMEDB358 Integrated and biological approach to diseases Gourdin Maximilien Pierson Audrey Lambert De Rouvroit Catherine Desseilles Martin 2 30h th. + 15h ex. SBIOB345 Human cell biology Renard Henri-François 2 15h th. + 10h ex. SBIOB344 Visits to laboratories, industry and hospitals Renard Henri-François 2 20h ex. SBIOB332 Mechanisms of cell responses to stimuli Michiels Carine Renard Patricia 2 15h th. + 10h ex. -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 SBIOB343 Conservation and Population Genetics Dennis Alice 2 14h th. + 10h ex. SBIOB003 Pluridisciplinary scientific field trip Yans Johan Silvestre Frédéric Yans Johan Silvestre Frédéric 3 48h th. + 48h ex. SBIOB367_P36774 <unknown> Thoré Eli Dennis Alice Kestemont Patrick 3 24h th. + 15h ex. SBIOB368 Applied ecology Kestemont Patrick De Laender Frédérik 4 20h th. + 15h ex. SBIOB346 Biodiversity and invasive species De Laender Frédérik De Laender Frédérik Marescaux Jonathan 2 15h th. + 15h ex. SBIOB347 Introduction to ecotoxicology Silvestre Frédéric Thoré Eli Kestemont Patrick 2 15h th. + 15h ex. SBIOB349 Environmental biology course (including ornithology) Pigneur Lise-Marie 2 20h ex. SBIOB362 Ecoethology Thoré Eli 3 24h th. + 15h ex. -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 SBIOB372 Immunology of infection Muraille Éric 2 15h th. SBIOB369 Metabolic diversity and ecology of microorganisms Lima Mendez Gipsi 3 22h th. + 22h ex. SBIOB375 Internship rotations Hallez Régis De Bolle Xavier Matroule Jean-Yves Renzi Francesco Lima Mendez Gipsi 5 40h th. SBIOB371 Bacterial pathogenesis De Bolle Xavier Renzi Francesco 2 15h th. SVETB313 Applied microbiology Gillet Nicolas 2 20h th. SBIOB370 Bacterial models Matroule Jean-Yves Matroule Jean-Yves 2 15h th. + 30h ex. SBIOB327 Genetic and epigenetic regulations Poncin Katy FINET Olivier Yague-Sanz Carlo 2 30h th.
-
-
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 FINT0043 Global change and the Anthropocene Yans Johan Dendoncker Nicolas Houssiau Laurent Linard Catherine Henry Sabine Poulain Amael Yans Johan 3 24h th. SBIOB003 Pluridisciplinary scientific field trip 3 48h th. + 48h ex. SBIOB350 Tutoring in biology Silvestre Frédéric 3 24h ex. Soft skillsFINT0049 Science for all : Effective science communication in English Hansel Aude Schutz Natassia 3 12h th. 12h th. FINT0048 Artificial intelligence: challenges and opportunities Frenay Benoît 3 24h th. Soft skillsSBIOB002 Professional observation internship Silvestre Frédéric 3 -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 SVETB306 Immunologie Gillet Nicolas 4 24h th. + 6h ex. SBIOB304 Bachelor thesis Messiaen Johan 5 SVETB310_P34593 Partim "Virology Gillet Nicolas 2 17.5h th. SBIOB305 Evolution Dennis Alice 2 15h th. SBIOB312 General Biochemistry II Arnould Thierry 5 25h th. SBIOB323 Cell Biology Messiaen Johan Renard Henri-François 5 45h th. + 10h ex. SBIOB326 Complements of genetics De Bolle Xavier 4 35h th. + 30h ex. -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 SBIOB309 Ecology course Kestemont Patrick 3 60h ex. -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 SVETB343 Internship at the Centre de Recherches Ovines 1 PETIT Astrid 1 20h ex. SVETB297 Zootechnics course 1 Muylkens Benoît 2 5h th. 5h th.
-
-
-
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 SBIOB324 Advanced statistics in life sciences Lima Mendez Gipsi 5 36h th. + 24h ex. -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 Soft skillsSELVB301 Writing and Presenting a Scientific Literature Review (level B2) Hansel Aude Schutz Natassia 2 15h th. 15h th. -
<unknown>
Code Name Staff Credits Hours/Quarter 1 2 SSPSB309 Ethical Leyens Stéphane LAURENT Nathanaël 2 15h th. SSPSB308 Philosophy of science Sartenaer Olivier 2 15h th. SSPSB307 Formal logic Sartenaer Olivier 2 15h th.
Biologists' professions
A constantly evolving sector
The life sciences are constantly evolving, and with them the techniques and professions. In Belgium, the pharmaceutical industry employs over 29,000 people, including more than 5,000 in research and development (R&D). With 12.8% of the world's pharmaceutical exports, Belgium occupies a leading position. Alongside the healthcare sector, the development of environmental awareness is opening up a growing number of opportunities for biologists.
Advancing science
Nearly 40% of our young graduates start their careers in research at university, in Belgium or abroad. There, they complete a doctorate (usually 4 years) or take part in a research program, most often on a fundamental subject.
Research is also carried out in corporate R&D departments and public research centers. Working as part of a team, biologists develop new products or carry out laboratory analyses.
I joined a CRO (Contract Research Organisation) in Louvain-la-Neuve right after graduating. I set up clinical studies on behalf of our customers. In concrete terms, I organize the submission of the study to the ethics committee. Then I train the people at the study site. I visit the site regularly to ensure that the protocol is being followed. I liaise with the other sub-contractors involved (e.g. for genetic analyses of blood, encoding of results in databases, etc.). Finally, I coordinate the writing of the final study report. It's a job that requires a lot of organization and a solid ability to manage stress
Marie, graduate
I manage a river contract in southern Belgium, within a nature park financed by European funds. Setting up a river contract involves convincing many partners with often divergent interests. I have to promote the project, notably by publishing brochures. I organize awareness-raising activities, such as courses for children. Administrative and financial management, as well as fund-raising, take up a good part of my time.
Nicolas, graduate
At the periphery of research and development
There are many service providers involved downstream from R&D. In large companies, departments are set up to manage the R&D process. In large companies, departments take charge of these activities, in whole or in part.
CRO's (Contract Research Organisation) are service companies that subcontract certain stages of clinical research on behalf of major companies. Some have specialized in managing the clinical studies to which new pharmaceutical products are subjected before they are put on the market, in order to verify their safety and pharmacokinetic profile (fate of a drug's active substance within the body, after administration).
Quality is the watchword of the pharmaceutical sector. We must always be able to prove that all procedures comply with current regulations, from the earliest stages of development right through to the delivery of products to customers.
Within the regulatory affairs departments, biologists supported by legal experts monitor current regulations and take charge of filing and monitoring "quality" or "intellectual property" dossiers with the relevant administrative authorities.
Preserving living heritage
More and more biologists are working to protect the natural heritage of plants and animals. In line with environmental policies, they are responsible for inventorying, managing, monitoring and promoting this heritage. They can lead large-scale projects linked to sustainable development (partner search, fundraising, animation, etc.).
My company develops bioreactors. There are 80 of us today. After a year's laboratory training, I manage a cell culture project. This involves planning the stages according to resources in terms of equipment and personnel, with the help of project management tools. I conduct bibliographical research and experiments, and present the results in presentations and publications. English is essential for all contacts with our partners and customers.
Florence, graduate
I'm a quality assurance manager at an agronomy research center. We test pesticides before they are put on the market. I spend 25% of my time in the field, inspecting in the laboratory, in meetings or on external audits. The rest of the time is spent writing procedures and reports. Communication, both oral and written, is essential in my job.
Vanessa, graduate
Transmitting a passion for living things
Science teaching remains a significant outlet for our degrees, both at Hautes Écoles and in upper secondary education.
The emergence of new professions
In recent years, we've seen biologists join the hospital world, either in medically assisted reproduction laboratories or in the management of clinical studies on sick patients.
The bioinformaticians, who combine their scientific training with solid skills in databases as well as statistics and programming, play a fundamental role in the face of the influx of new genomic sequencing and other data resulting from the exploration of living things. They model and compare this wealth of information with the aim of posing relevant research hypotheses to be tested in experimental settings.
I'm a biologist in the molecular biology department of the Institute of Pathology and Genetics (IPG). One of the IPG's missions is to screen for diseases of genetic origin (cystic fibrosis, for example) in adults, children, newborns and fetuses. As a biologist, I have to manage the work of a team of laboratory technologists, analyze the results obtained for each patient and communicate them to the doctor in charge in the form of a report. We also have to keep abreast of new scientific and technical developments through literature searches, training courses and conferences. Managing the time and resources at our disposal, as well as the ability to communicate scientific data concisely, are essential skills in this profession.
Charlotte, graduate